Methods of control of meat borne diseases
The following four measures can prevent meat borne diseases.
1.CLEAN
Wash hands and meat contact surfaces and utensils often, between tasks, and if they have become contaminated. Effective cleaning involves removing soil and debris, scrubbing with hot soapy water and rinsing, using potable/drinking water. Sanitizing involves the use of high heat (e.g., a dishwasher) or chemicals (e.g., chlorine bleach) to reduce or eliminate the number of microorganisms to a safe level.
- Wash hands with warm water and soap for 20 seconds and dry with a disposable paper towel or clean hand cloth.
- Alcohol based hand sanitizers are not a replacement for They are not effective if the hands are dirty, they are not effective against Norovirus, and they do not eliminate all types of microorganisms.
- Wash cutting boards, dishes, and utensils after preparing each food item and before you use it for the next meat product.
- Use hot, soapy water, rinse with hot water, and air dry or dry with a clean paper towel or clean dish cloth or wash in the
- Wash countertops after preparing each meat item and before you use it for the next.
- Use paper towels or clean dish cloths to wipe kitchen surfaces or spills.
- Wash countertops with hot soapy water, rinse with hot water and air dry or dry with a clean paper towel or clean dish cloth.
- To sanitize for added protection for bacteria on surfaces, you can use : Dilute mixtures of chlorine bleach and water . Alternatively, commercial products for sanitizing the home kitchen are available. Follow manufacturer instruction for use.
2. SEPARATE
Separate dishes to prevent cross contamination. Cross contamination is the transfer of harmful bacteria from uncooked food products (e.g. raw meat, fish, and poultry) or unclean people, countertops, and kitchen equipment to ready-to-eat food
Prevent cross contamination when grocery shopping.
- Physically separate raw meat, fish and poultry to prevent their juices from dripping onto other foods. This can be done by:
- Segregating raw meat, fish and poultry on one side of the shopping cart.
- Placing raw meat, fish and poultry in separate plastic bags (e.g. one bag for chicken, one bag for fish, etc.).
- Designate reusable bags for grocery shopping only. Reusable bags for raw meat, fish, or poultry should never be used for ready-to-eat products.
- Frequently wash bags. Cloth bags should be washed in a machine and machine dried or air-dried. Plastic-lined bags should be scrubbed using hot water and soap and air-dried.
- Separate raw meat, fish and poultry in disposable plastic bags before putting them in a reusable bag
- Check that both cloth and plastic-lined reusable bags are completely dry before storing.
Prevent cross contamination when storing food in the refrigerator.
- In the refrigerator, store raw meats, fish, and poultry below ready-to-eat and cooked foods.
- When thawing frozen raw meat, fish and poultry, put the food in a plastic bag or on a plate on the lowest shelf to prevent juices from dripping onto other foods.
- After thawing in the refrigerator, food should remain safe and of good quality for a few days before cooking. Food thawed in the refrigerator can be refrozen without cooking, although quality may be impacted.
Prevent cross contamination when handling, preparing, and serving food.
- Thoroughly wash your hands before and after handling different foods, after using the bathroom, and anytime they can become contaminated.
- Use separate cutting boards for meat and produce. Alternatively, prepare produce first, then meat.
- Wash and rinse cutting board, knives, and preparation area after cutting raw meat, fish or poultry. These items can be sanitized after cleaning.
- Use a clean serving plate to serve cooked meat. Do not use the plate that held the raw meat, unless it is washed.
- Throw away any sauce or dip that has been used to marinade raw meat, fish, or poultry. Do not use this extra sauce as a dip for cooked food unless it is boiled first.
- COOK
Cook meat thoroughly and use a thermometer to verify the proper temperature was reached as indicated in the table below:
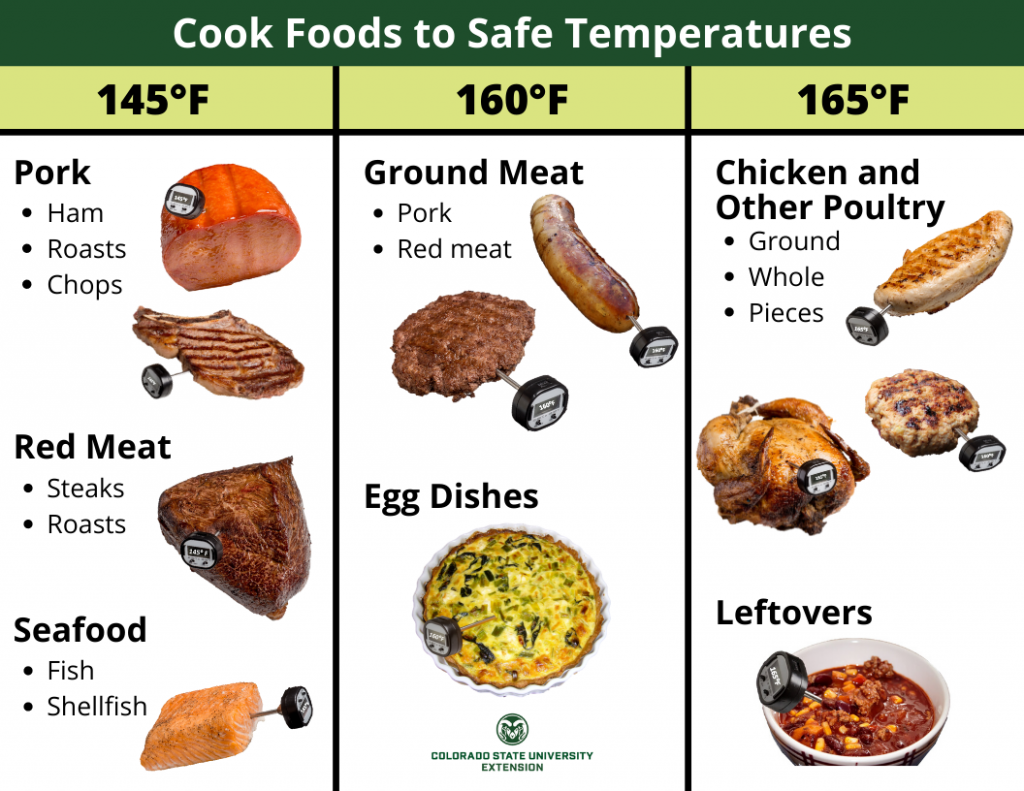
Clean your food thermometer with hot, soapy water before and after each use.
- CHILL
Chill foods promptly. Cold temperatures slow the growth of harmful bacteria. Cold air must circulate to help keep food safe, so do not over fill the refrigerator. Maintain the refrigerator temperature at 41°F or below. Place an appliance thermometer in the rear portion of the refrigerator, and monitor regularly. Maintain the freezer temperature at 0°F or below.
- Refrigerate and/or freeze meat, poultry, eggs and other perishables as soon as possible after purchasing.
- Consider using a cooler with ice or gel packs to transport perishable food.
- There are three safe ways to thaw food: in the refrigerator (see Separate), in cold water, and in the microwave.