Erythrocyte Count (RBC count)
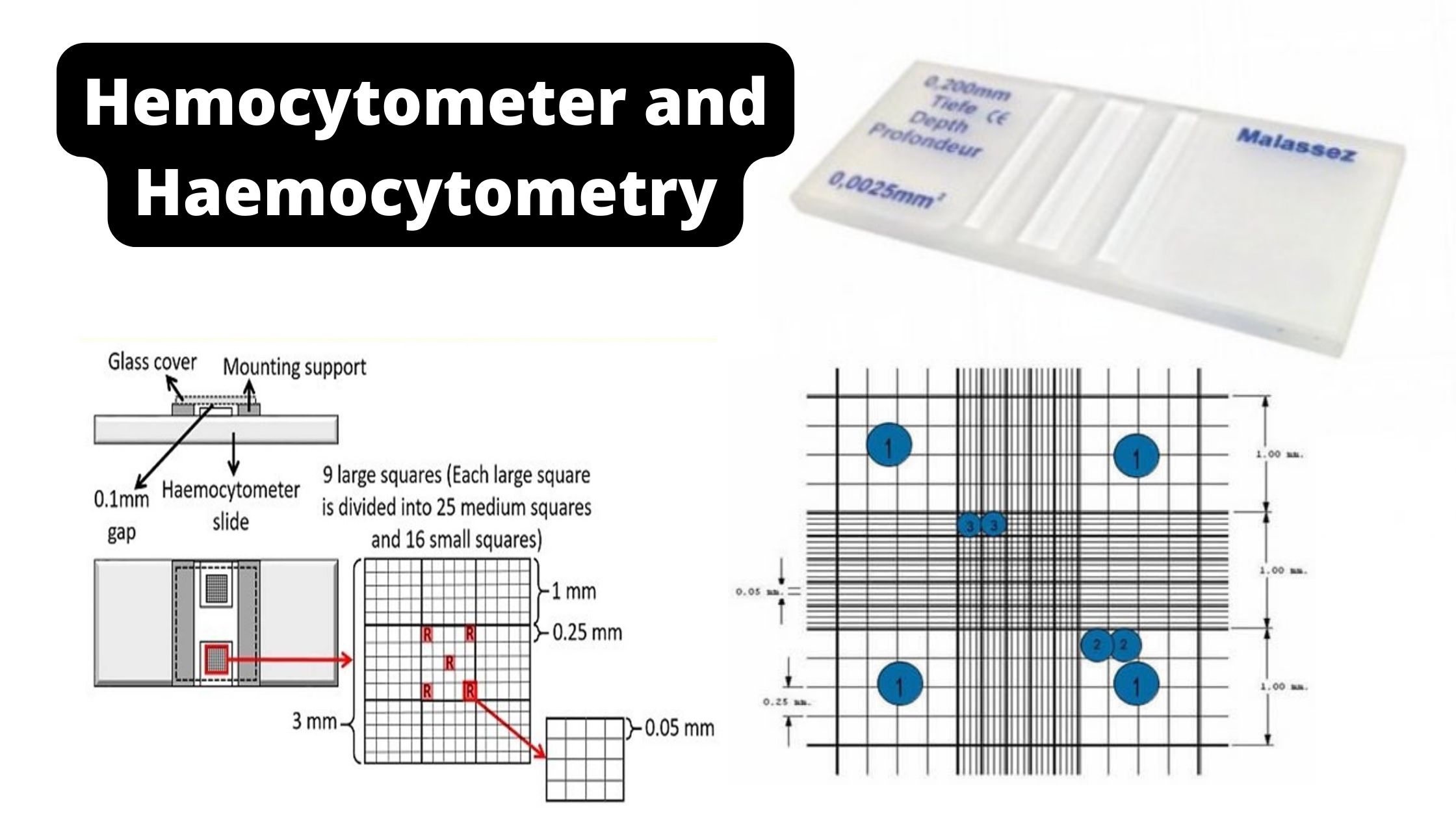
RBCs are counted using a special chamber designed to count blood cells within specimen. This chamber is called Neubauer’s chamber or Hemocytometer.
Materials Required:
- Hemocytometer or Neubauer’s chamber
- Micropipette
- RBC diluting fluids or Hayem’s fluid
- RBC pipette
- Glass cover
- Blood sample
Procedure:
- First RBC pipette is filled with blood upto 0.5 mark and external part of pipette is wipe out
- Same pipette is then filled with RBC diluting fluid upto 101 mark
- Blood and diluting fluid are then mixed gently by turning pipette horizontally between palm of hands.
- Hemocytometer is then prepared by removing from case and cleaning with soft cotton gauze or swab.
- Clean cover glass is then placed on top of Hemocytometer’s lined region.
- 1-2 drops of blood are discarded during loading Hemocytometer. Rubber of RBC pipette are gently pressed down until fluids are in hanging position. Tip of pipette should touch against edges of coverglass
- Small amount of sample is then placed on edges of coverglass and wait for 3-5 minutes in order to settle down RBC in chamber
- Prepared slide is then observed under microscope to count RBC
Counting of RBC under microscope:
First chamber is focused on 10X. First focus on five small square of central square to count RBC under 40X.
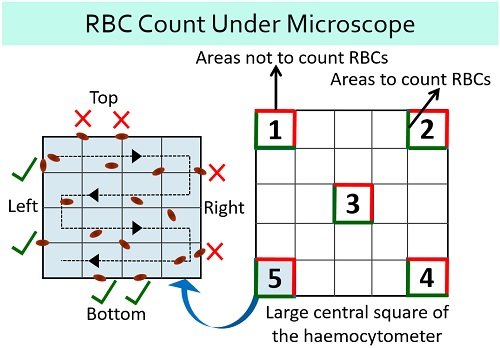
Counting of cell in L-shape of each square is done. Cells touching top, bottom and right side of square is discarded. After counting of cell, number of RBC is then calculated using formula;
Total RBC/µL= Number of RBC counted * Dilution factor/Area * Depth
- Given, dilution factor= 1:200 or 200
- Area; large central square is sub-divided into 25 small or medium squares. So area will be one sq mm. number of RBC counted in 5 small square out of 25 squares. So area will be 5/25 or 1/5 sq mm
- Depth: 0.1 mm
- Total RBCs = N x 200/1/5×0.1 = N x 200 x 50= N x 10,000 cells/µL