Aspergillosis :
- It is a disease caused by infection with genus Aspergillus.
- Manifestation of aspergillus depends upon which organs or system are involved and whether infection is localized or disseminated.
- It is usually confined to the lower pulmonary system with florid lesions in air sacs and lungs.
- In young poultry, it is referred to as brooder pneumonia .
- Other synonym :
- Fungal or mycotic pneumonia
- Pneumonomycosis
- Bronchomycosis

- Less manifestation related to infections of eye , brain , skin , joints and viscera.
- It usually means ‘pulmonary or respiratory aspergillosis’ .
Etiology :
Two major species : Aspergillus fumigatus
A . flavus
Other : A. terrus , A. glaucus , A. niger
- Organisms are common soil saprophytes occurring in decaying vegetable matter and feed grains.
- They grow on organic matter in warm humid environments .
- Spores are highly resistant to disinfectant .
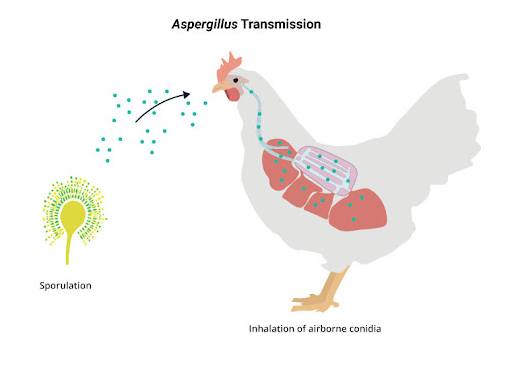
Transmission :
- Infections are acquired from environmental exposure.
- Infection is by inhalation of spores that usually originate from infected eggs.
- Contamination of equipment may result in hatchery infection.
- Accidental breakage
- Entry through egg shell
- Contaminated feed or poultry house litter also produce infection.
Clinical signs :
- Biphasic mortality pattern
Acute form :
- Inappetance
- Weakness / lethargy
- Silent gasping
- Rapid breathing
- Thirst
- Drowsiness
- Nervous sign (rare)
- Loos or change in voice path

Chronic form :
- Ocular discharge (ocular form only )
- Wasting
- Torticollis

- Due to hatchery infection ( within first 3-5 days infection )
⬇
Dyspnoea , polypnea, gasping ( open mouthed breathing – gaspers )
⬇
When these are associated with IB & ILT
⬇
Gurgling and rattling noises
[ In Aspergillus, usually no sounds ]
Postmortem lesion :
- Yellow to gray nodules or plaques in lung , air sac , trachea , plaque in peritoneal cavity, may have greenish surface.
- Conjunctivitis / keratitis
- Brain lesions may be seen in some birds with nervous signs.
- Air – filled cavities may appear green to black due to development of pigmented conidiophores.
- Brain : white to yellow circumscribed area either in cerebellum or cerebrum .


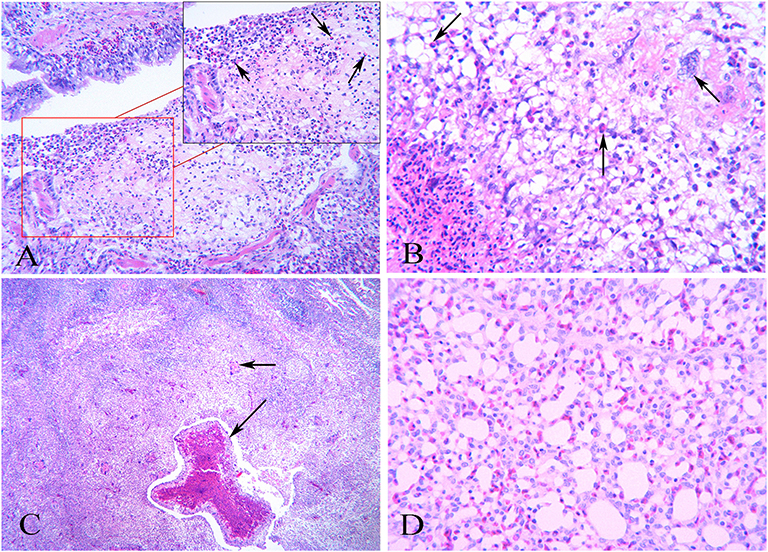
Microscopic :
- Air sacs : thickening due to massive infiltration of heterophil , multinucleated giant cells and other types of leukocytes.
- Germinating conidia are seen in membrane interstitium and lymphohistiocytic perivascular in less severely affected areas.
- Granuloma composing central necrotic cellular debris and heterophil with peripheral palisade of epithelioid macrophages and aggregates of lymphocytes .
Diagnosis :
- Clinical signs
- Lesions : white caseous nodules in lungs or air sacs
Exudate plugs in tracheal and bronchial lumen.
- Demonstration of branched , septate Aspergillus hyphae in lesions.
- Confirmation should also be made by cultural isolation and identification of causative agents.
- Serological test ( limited value )
DDx :
From other respiratory disease by granulomatous lesions at necropsy
a. Exudative fibrinous or purulent air sacculitis and pneumonia are frequently seen in :
- Mycoplasmosis
- Colibacilosis
- Fowl cholera
- Chlamydiosis
- Infectious bronchitis
- Newcastle disease
- Infectious laryngotracheitis
b. If granulomatous lesions predominate then
- Mycobacteriosis