Mechanism of Apoptosis

Extrinsic Pathway (Death Receptor):
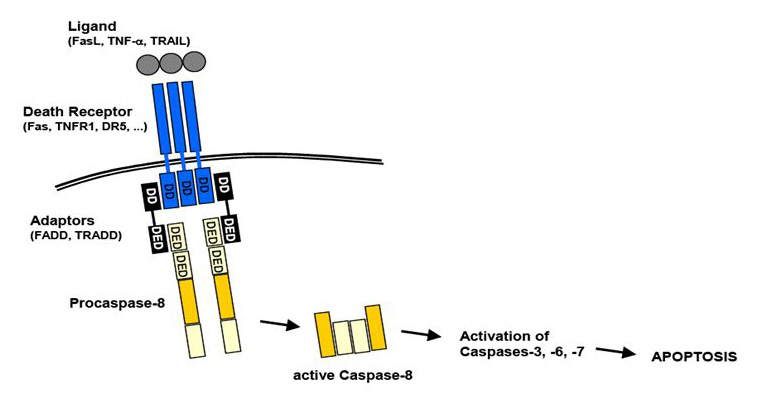
- Many cells express surface molecules, called death receptor that triggers apoptosis. Most of these are member of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family which in their cytoplasmic region contains “death domain” as it interacts with other proteins involved in cell death.
- Prototypic death receptor is type I TNF receptor and Fas (CD 95). Fas ligand (Fas L) is membrane protein expressed mainly on activated T-lymphocyte.
Binding of Fas-ligand with Fas receptor
Multiple molecules of Fas receptor come together due to cross-linking of Fas L and small cluster of Fas molecule occurs on membrane.
These molecules bind with adaptor protein via intracellular death domain
This in turn recruit caspase-8; in inactive form they are called pro-caspases-8. When intracellular death domain interacts with pro-caspases, pro-caspases becomes activated. These are called initiator caspases.
Initiator caspases interact with other caspases and activate them. Activated caspases are called executioner caspases.
Activated caspases digests away protein that acts as cytoskeleton of cytoplasm and nucleus. They also digest inhibitory component of DNases. These DNases after activation breakdown genetic material of cell. It starts to cut nucleosome, which is very characteristic of apoptosis. It is called internucleosomal breakdown of DNA.
As cytoplasm, nucleus DNA breakdown, cell membrane undergoes alteration and forms blebs around it. These blebs then separate out which is called apoptotic bodies.
Apoptotic bodies secrete opsonin which gets plastered on outer surface of apoptotic bodies. Macrophages have receptor for these molecules. These opsonin strongly bind with macrophages receptor and then macrophages get activated and engulf them.
Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis:
- Mitochondria plays important role in this pathway so called as mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.
- Mitochondria contain several proteins that are capable of inducing apoptosis. It includes Cytochrome-C and other proteins that neutralize endogenous inhibitor of apoptosis. (AIF- Apoptosis Inducing Factor).
- Choice between the cell survival and cell death is determined by the permeability of mitochondria. It is controlled by family of more than 20 proteins prototype Bcl-2.
- Pro-apoptotic genes also called prodeath genes when expressed, cell undergoes apoptosis. These genes include Bak, Bax, Bad. These genes are controlled or balanced by anti-apoptotic genes (pro-life genes).
- Product of anti-apoptotic gene forms dimer that plug the channels in mitochondrial membrane until these channels ae plugged well, AIF cannot express and cell continues living.
- Also, Bcl-2 products also keep inhibiting apoptosis activating factor (protein normally present in cytosol).
- Bcl-2 product and Bad, Bax, Bak forms heterodimers that plugs the permeability channel in mitochondria and inhibit AIF and cytochrome “C” to come/escape into cytosol.
- Until there is growth factor, hormones survival signals are acting on cell, intracellular signaling keep pro-apoptotic gene inhibited and anti-apoptotic gene activated.
When cells are deprived of growth factor and other survival agent or exposed to agents that damage DNA or accumulate unacceptable amount of misfolded protein, number of sensors are activated. These sensors are called ‘BH3 proteins’, member of Bcl-2 family.
This causes blockade in stimulation of ant apoptotic gene. Due to this their concentration starts to decline and pro-apoptotic genes starts to express in higher numbers.
Pro-apoptotic genes start to produce more products. They dimerize, insert into mitochondrial membrane and forms channels through which cytochrome ‘c’ and AIF are escaped into cytosol.
Also, cytochrome ‘c’ together with some cofactors and AIF, acts on initiator caspase; caspase-9.
Caspase-9 activates another series of caspases that are called executioner caspases.
Executioner caspases digest away cytoskeleton of cytoplasm, nucleus. They also activate DNAases which breaks down DNA and nucleoproteins. This lead to fragmentation of cells.
Cell membrane forms blebs around it and separates out from cell, forming apoptotic bodies. These apoptotic bodies are then engulfed by macrophages and phagocytosed.
