Types of Metamorphosis
- Ametabolous / No metamorphosis:
- The metamorphosis in which there is gradual increase in size of young until adult dimension is maintained is called Ametabolous.
- Usually, there is no difference between young and adult except the size.
- Eg: Silver fish, sprint tails etc.
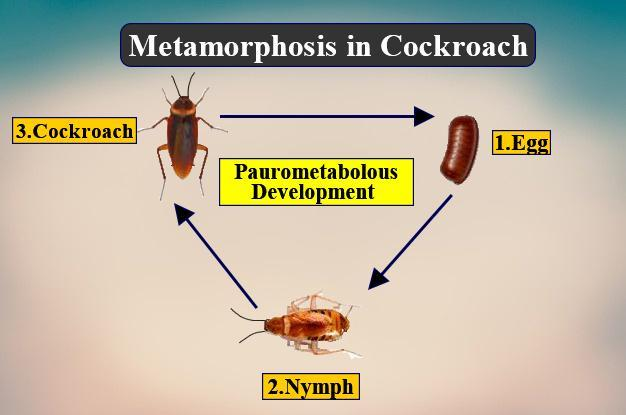
2. Gradual metamorphosis ( Paurometabolous ):
- The life cycle of insects with gradual metamorphosis have three life stages: egg, nymph and adult.
- Nymphs resemble the adult except that their body parts are out of proportion with each other, and they do not have fully developed wings and external genitalia.
- With each molt, the nymphs gradually develop wings and take on the body proportions of an adult.
- Nymphs have the same type of mouthparts as the adult, and they both feed on the same kind of food.
- Eg: Aphid, grasshoppers, termites, etc.
3. Hemimetabolous / Incomplete metamorphosis:
- The metamorphosis which consists of three stages i.e. egg, naiads and adult is called hemimetabolous.
- However, the adult insect with incomplete metamorphosis lays its eggs in or near water and the naiads develop in water.
- The adults are flying insects that live out of water.
- Naiads and adults therefore do not eat the same kind of food. Naiads have chewing mouthparts, but the adults have differently shaped chewing mouthparts or no functional mouthparts.
- The naiad and the adult usually differ a lot in appearance although the naiads gradually develop wings.
- Dragonflies, Mayflies, Stoneflies

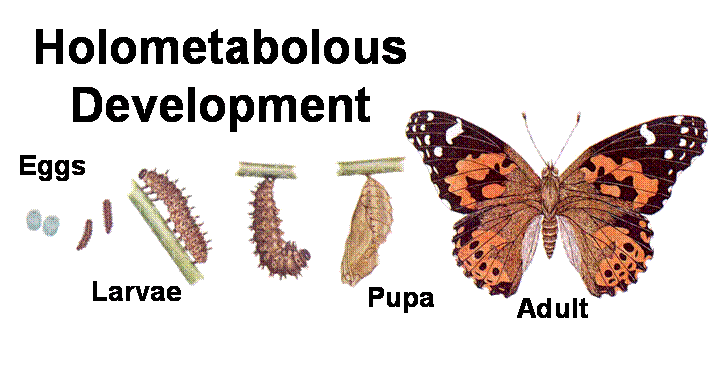
4. Holometabolous / Complete Metamorphosis:
- The Metamorphosis which consists of four distinct stages i.e. egg, larva, Pupa and adult is called Holometabolous.
- The larval stages do not look like the adult at all, and they are often worm-like.
- Larvae often have different mouthparts and food habits than the adult, and they often live in places different from the adult.
- Larvae molt several times and get a little larger with each molt, but there is no gradual development of wings or other adult characteristics.
- When a fully grown larva molts, it changes into a pupa.
- The pupa usually does not eat or move around much, but a lot of internal changes take place.
- When the pupa has made all its internal changes, its skin splits and the fully formed adult emerges.
- Most insects with complete metamorphosis are winged in the adult stage.
- The adults do not molt or grow any more.
- Little flies or beetles, for instance, do not grow to become larger. Flies (Diptera), beetles (Coleoptera), wasps (Hymenoptera) and butterflies (Lepidoptera), have holometabolic life cycles.