Pestes de Petits ruminant (PPR)
- Also known as goat plague
- Contagious disease of goat and sheep.
- Goats are more susceptible than sheep.
a) Etiology:
- Morbili virus ( Paramyxovirisae family)
b) Transmission:
- Close proximity is necessary as virus doesn’t survive long outside the host.
- Virus excreted by urine, Faeces, nasal discharges and sweat.
- Transmission occurs by
a) Inhalation of infected droplets
b) Ingestion of contaminated feed
c) Pathogenesis:
- Entry of virus via ingestion or inhalation à Localizes on upper respiratory tract à Multiply in epithelial cells of URT à Enter to blood leading to viremia à from blood, localizes in target organ à Virus multiplies and develop clinical signs in 3-9 days
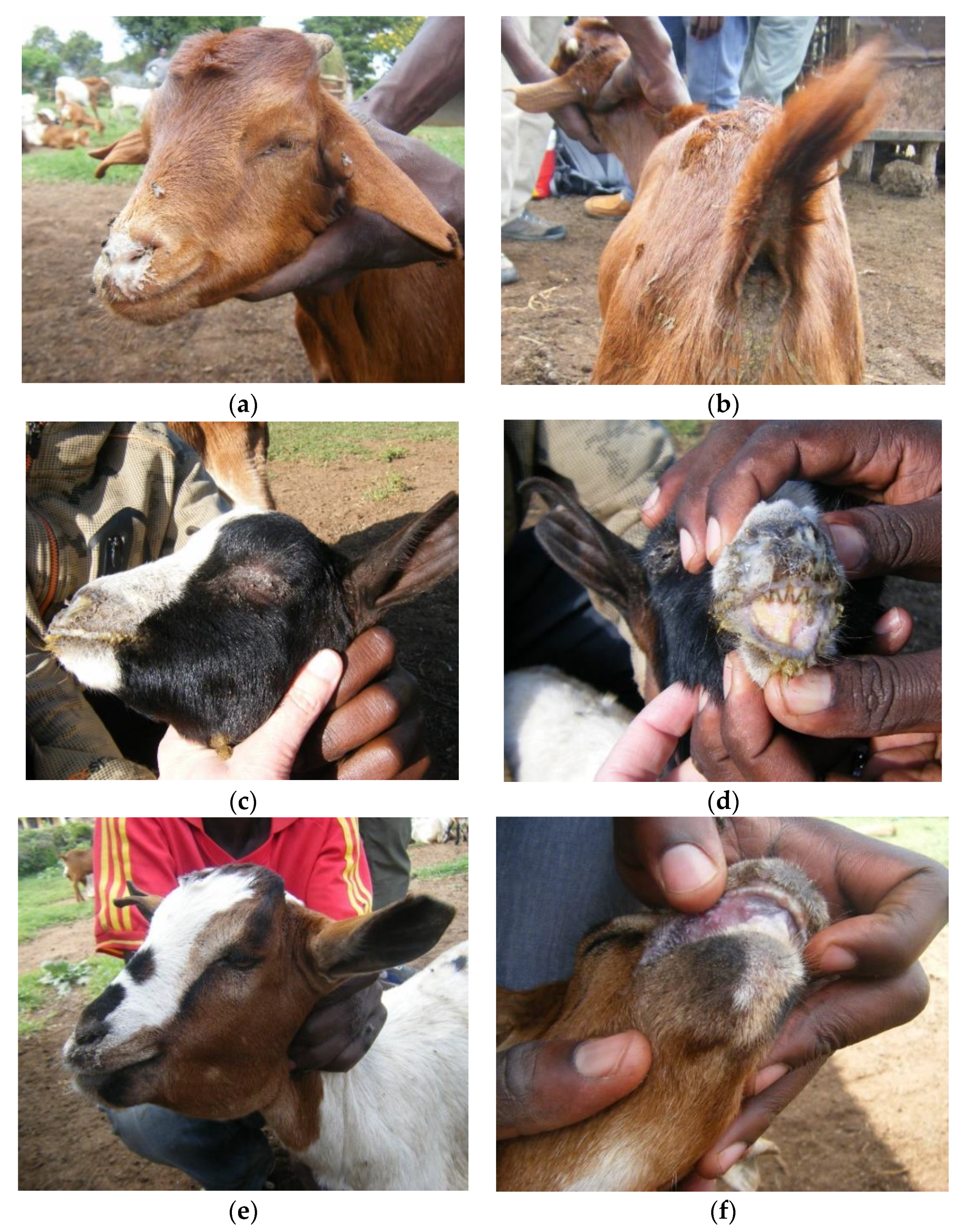
d) Symptoms:
- Incubation : 3-10 days
- High fever ( > 1040F)
- Occulonasal discharge ( inflamed eye membrane)
- Necrotic stomatitis ( tongue and pharynx)
- Respiratory distress
- Diarrhoea
- Leukopenia but not as marked as in rinderpest
- Early mouth lesions showing areas of dead cells.
e) Diagnosis:
- Clinical signs and lesions
- Isolation/ identification of virus
- ELISA test
f) Differential diagnosis:
- Rinderpest
- FMD
- Blue tongue disease
- Coccidiosis
g) Prevention and treatment:
- Quarantine
- Disinfect the surrounding
- Vaccination
- Slaughter the infected animal
- Carcass burned or bury the animal