Downy mildew of maize

Sorghum DM – Peronosclerospora sorghi / P. philippinensis
- sorghi causes sorghum downy mildew, which can result in severe economic losses of both sorghum and maize.

Crazy top DM – Sclerophthora macrospora
- It causes downy mildew on a vast number of cereal crops including oats, rice, maize, and wheat as well as varieties of turf grass. The common names of the diseases associated with Sclerophthora macrospora include “crazy top disease” on maize and “yellow tuft” disease on turf grass.

Brown stripe DM – Sclerophthora rayssiae var zeae
- The first record of brown stripe downy mildew of maize occurred in India in the early 1960s. S. rayssiae var. zeae has been identified on leaves of Zea mays subsp. mays in India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Thailand.

Sugarcane DM – Peronosclerospora sacchari
- It cause downy mildew on Sugarcane and Maize.
Symptoms:
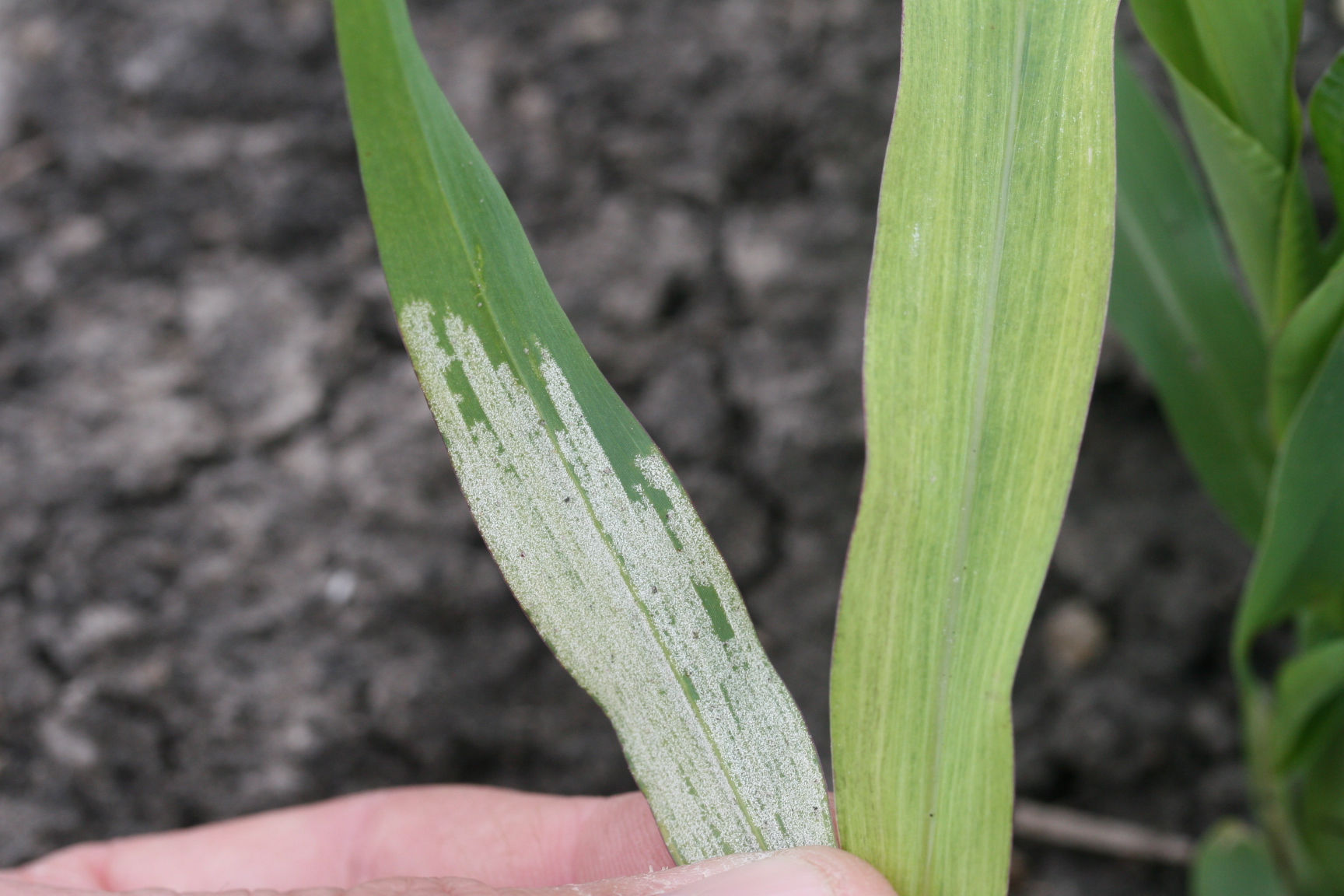
- Development of chlorotic streaks that appears on the leaves and the plants exhibit a stunted and bushy appearance due to the shortening of the internodes.
- White downy growth can be seen not only on the lower surface of leaf but also on the chlorotic streaks.
- Affected leaves often tear linearly causing leaf shredding.
- The downy growth also occurs on bracts of green unopened male flowers in the tassel.
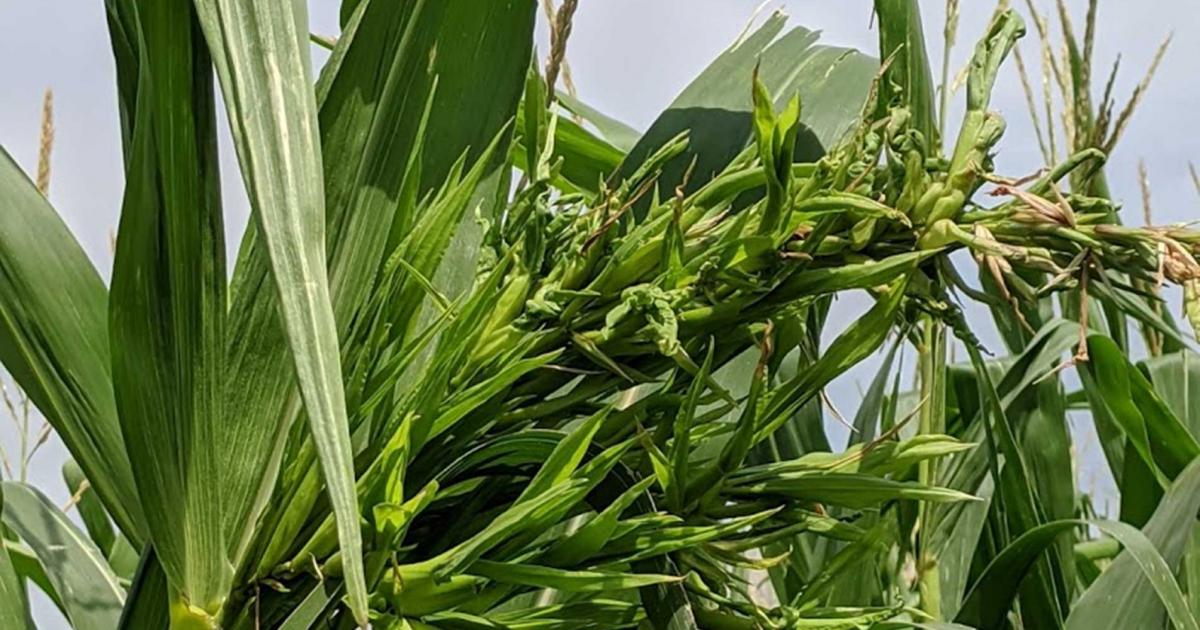
- The important symptom of the disease is the partial or complete malformation of the tassel into a mass of narrow, twisted leafy structures.
- Proliferation of axillary buds on the stalk of tassel as well as the cobs is very common (Crazy top)
Pathogen:
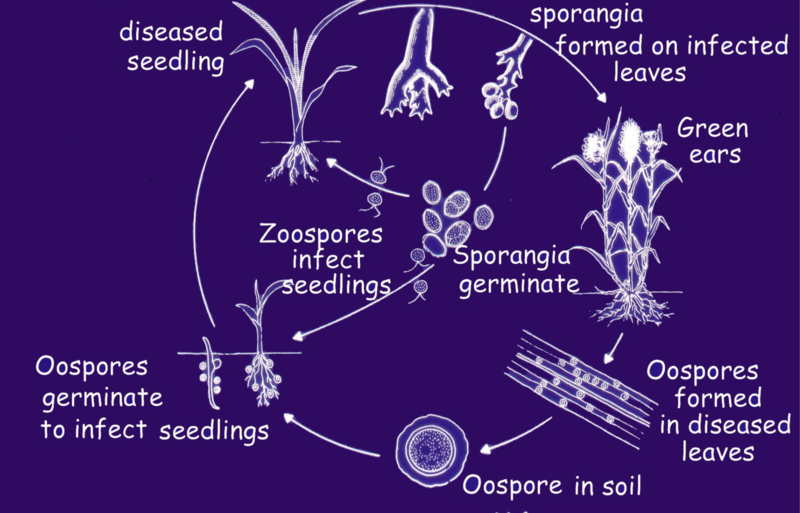
- The fungus grows as white downy growth on both surface of the leaves, consist of sporangiophores and sporangia.
- Sporangiophores are quite short and stout, branch profusely into series of pointed sterigmata which bear hyaline, oblong or ovoid sporangia (conidia).
Favourable Conditions:
- High relative humidity (90 per cent).
- water logging condition.
- light drizzles with a temperature of 20-250C favours the disease development.
- Young plants are highly susceptible.
Spread and Survival:
- Survive: soil, plant debris and graminaceous collateral hosts (Sorghum bicolor, Sorghum halapense, etc). The oospores survive in the soil as well as in the infected plant debris.
- Spread: air-borne conidia.
Management:
- Crop rotation with pulses
- Grow resistant hybrids like DHM-1, DHM-103, DMR-5 and Ganaga II.
- Seed treatment with Metalaxyl (Apron 35SD) at 4g/kg of seeds.
- Spray the crop, 3-4 times, with Metalaxyl MZ (Ridomil MZ)@0.2% starting from 20th day after sowing.