Southern leaf blight
C/O: Bipolaris maydis (telomorph: cochilobus heterostropus)
Symptoms:
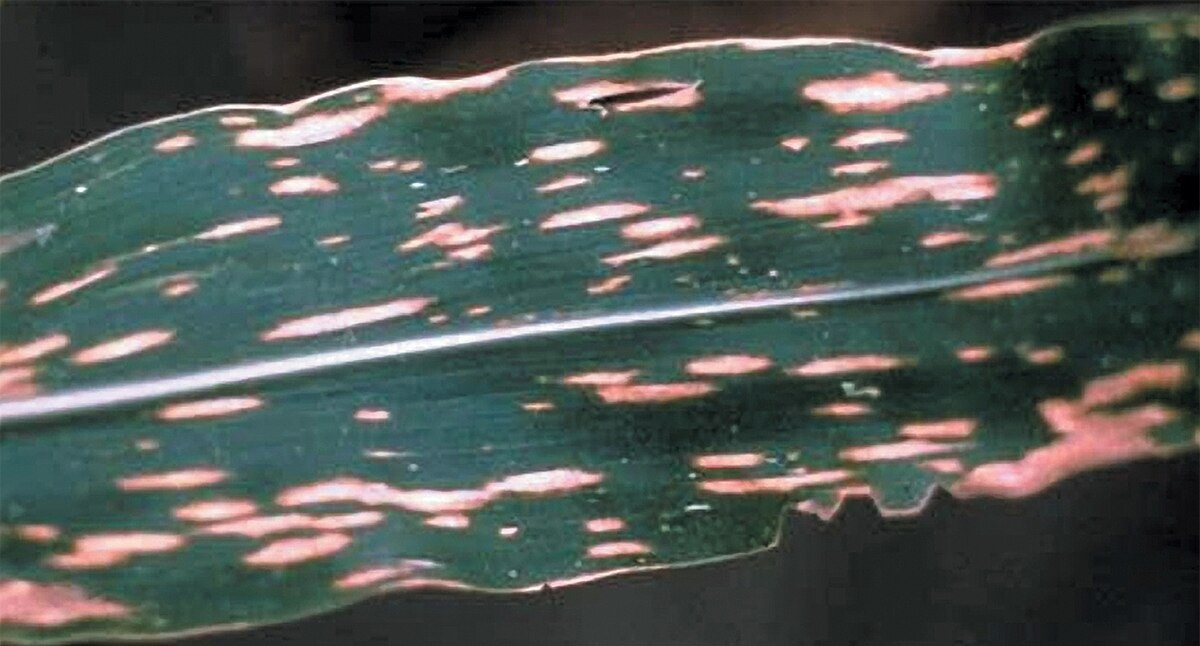
- Spots are smaller, yellowish round or oval spots in the beginning, variable in color and pattern
- These spots enlarge, become elliptical and the center becomes straw colored with a reddish-brown margin.
- Spots may be round to elongated and may be vein limited, have more or less parallel margins
- Conidia and conidiophores are formed in the center.
- Spots may be 2 mm to 22mm in size
- Reddish brown margin of spots may be seen
- Tassel infection is rare and no ear infection is reported.
Etiology:
- Facultative saprophyte
- Conidiophores: 2-3 in number, emerge from stomata, brown in color
- Conidia: curved and septate.
Favorable condition:
- Thrives in warm, moist-temperate or subtropical corn-growing environments.
- Warm temperature – 20-34 0C
- In contrast, long and sunny growing areas with dry conditions are highly.
Survive and spread:
- Survive: Perithecium containing asci with ascospores and conidiophore as resting stage which present on soil, crop debris etc.
- Spread: wind borne conidia through wind and splash of rain.
Disease cycle:
- Polycyclic disease.
Management:
- Reduce inoculum by managing infected debris, destroying collateral and alternate host, maintaining proper spacing
- Use of resistant varieties: Manakamana-3, Ganesh-1, Ganesh-2
- Seed treatment with Carbendazim 50% WP (Bavistin) 2gm/kg of seed.
- Foliar application of fungicides like mancozeb, propiconazole and zineb have been found to be effective against southern leaf blight of maize.