Diseases of Jackfruit
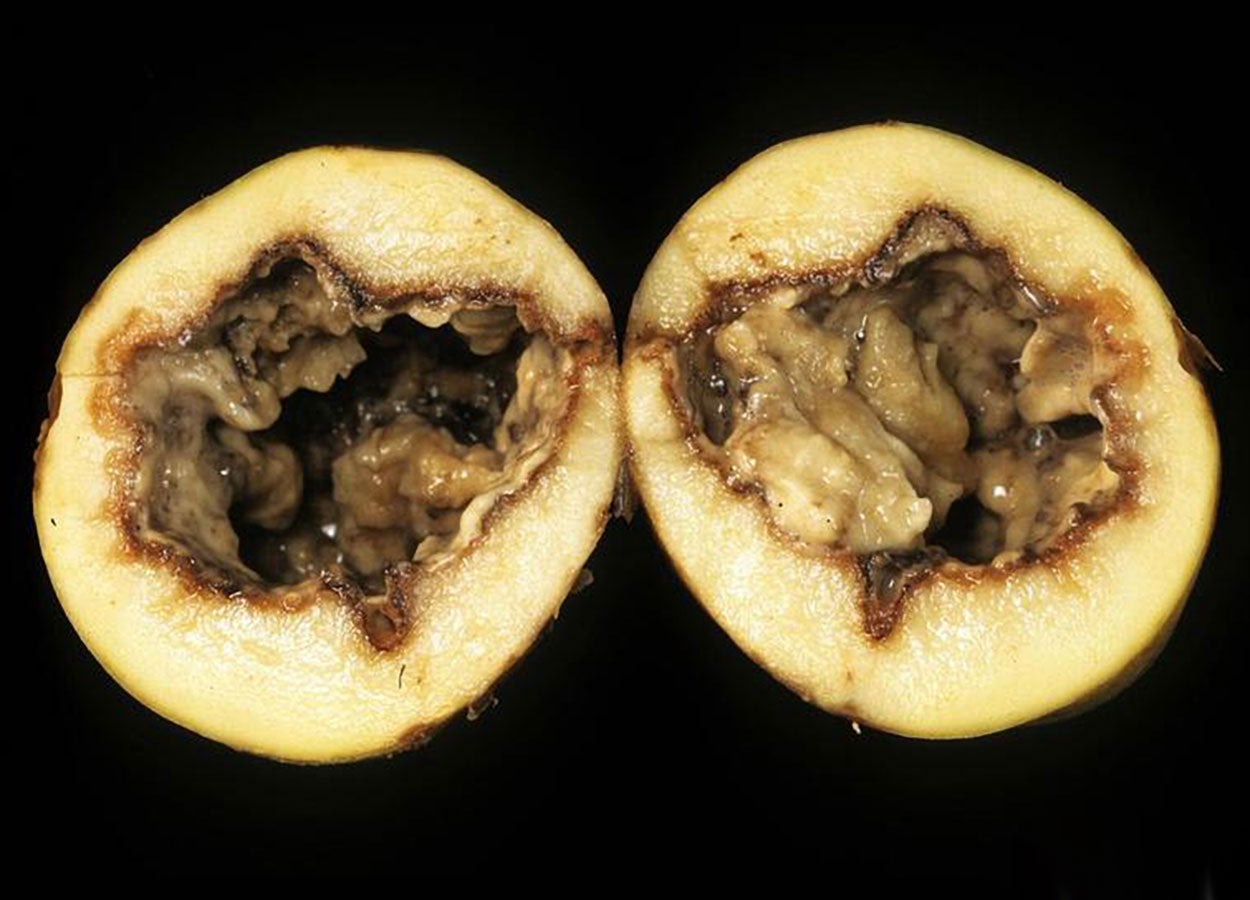
a) Soft rot or fruit rot:
- Young fruits and male inflorescences are badly attacked by the soft rot or fruit rot: fungus and only a small percentage of the fruits reach maturity.
- Female inflorescence and matured fruits are not usually attacked.
- The disease is a soft rot. A large number of the affected fruits falls off early. In the first stage of attack ·the fungus appears as greyish growth with abundant mycelia which gradually becomes denser forming a black growth.
b) Dieback:
- The most of die-back becomes evident by discoloration and Dieback darkening of the bark some distance from the tip.
- The dark area advances and young green twigs start withering first at the base and then extending outwards along the veins of leaf edges.
- The affected leaves turn brown and their margins roll upwards.
- At this stage, the twig or branch dies, shrivels and falls.
- There may be exudation of gum from affected branches. Such branches are often affected by shoot borers.
- Infected twigs show internal discoloration.

c) Leaf spot:
- Produces dark brick red spots on both the surface of leaf which Leaf spot upon maturity become greyish studded with dark colour, pin headed fruiting bodies of the fungus.

d) Rust:
- Rust generally develops late in the summer, and in years whenRust disease is severe, it can cause the trees to defoliate in a matter of a few weeks. If this happens on a regular basis, the overall growth of the trees can be reduced and yields can be affected.
- Initially, symptoms of fig rust are visible as small, yellowish spots on the upper surface of the leaves. As these spots (or lesions) grow larger, they turn a reddish-brown color but remain relatively smooth.
- On the lower surface of the leaf, the lesions are a reddish-brown color and have a slightly raised, blister-like appearance. Heavily infected leaves often turn yellow or brown, particular y around the edges, and drop prematurely.
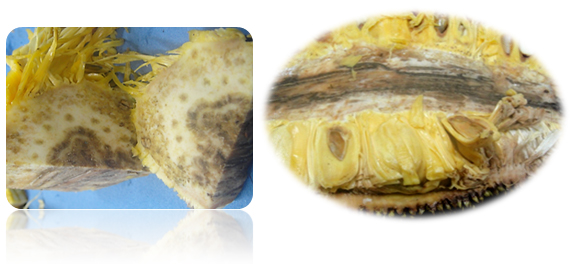
e) Pink disease:
- Disease appears as a pinkish powdery coating on the stem.
- Pink color represents profuse conidial production of fungus.
- Young woody branches of the affected trees lose their leaves & show die back symptoms.
- Pink encrustation is seen on the lower shaded side.
