Types of Caudal fin
(A) – Heterocercal,
- The heterocercal tail is sometimes called the shark-tail type of caudal fin. Elasmobranch (cartilaginous fish) and some primitive type of bony fishes contain this type of fin.
- This fin has two unequal lobes where the upper smaller lobe is known as epichordal lobe and a much larger lower lobe is known as hypochordal lobe.
- In this case, the hind end of the vertebral column becomes bent upwards and continues almost up to the tip of the fin.
(B) – Protocercal,

- It is the most primitive type of caudal fin where the straight vertebral column divides the caudal fin into two equal lobes such as upper lobe and lower lobe.
- In this case, the upper lobe is known as epichordal or epicaudal and the lower lobe is called hypochordal or hypocaudal lobe.
- A series of rods are arranged around the central axis of the caudal region, which support the fin membrane.
- Undoubtedly, during the developmental period, the caudal fin of all fishes passes through the protocercal stage. This type of fin is found in cyclostomes and the living dipnoans(lungfishes).
(C) – Homocercal,
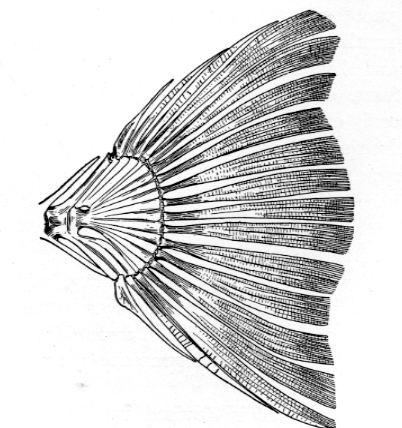
- Most of the higher teleosts have homocercal caudal fin.
- It has superficially symmetrical and two equal sized lobes such as upper epichordal and the lower hypochordal lobe.
- Internally, this tail is asymmetrical and the hinder end part of the vertebral column is greatly shortened and turned upward.
- In this case, the vertebral column does not touch the posterior limit of the fin.
(D) – Diphycercal
- Sharks possess a heterocercal caudal fin.
- The dorsal portion is usually larger than the ventral portion
- The high-performance bigeye tuna is equipped with a homocercal caudal fin and finlets and keels.