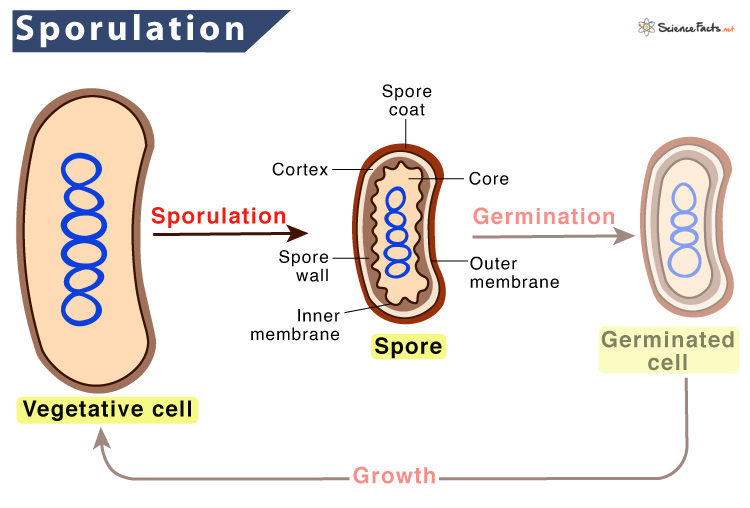
Sporulation in bacteria:
Starvation (unfavorable condition) initiates sporulation in bacteria. It is a 8-9 hrs genetic program that ultimately yield a spore (endospore). Sporulation process has eight morphological stages:
- Stage 0: point at which vegetative cell decides to use polar division sites to begin septum formation.
- Stage I: replication and stretching of DNA along length of cell.
- Stage II: septum forms unequal compartments. The small compartment give rise to spore (forespore) and larger to mother cell. Each compartment contains chromosome.
- Stage III: mother cell membrane engulfs forespore.
- Stage IV: destruction of mother cell chromosome and cortex ( heat resistance and maintain dormancy) formation between two membranes (own membrane + membrane of engulfing mother cell) of spore.
- Stage V: deposition of coat proteins on outer membrane.
- Stage VI: maturation and complete development of spore. Synthesis of dipicolinic acid (dehydration and dormancy maintainance).
- Stage VII: mother cell releases spore.