Colibacillosis :
Colibacillosis is an infectious disease caused by bacterium E. coli and is seen in poultry flocks worldwide.
- coli can cause an infection under skin ( cellulitis ) and is commonly associated with respiratory disease in birds; leads to septicemia and death.
- Primarily affects broiler chicken between the ages of 4-6 weeks.
Etiology :
Avian pathogenic E. coli
[ gram -ve , rod shaped , non-acid fast , non- spore forming bacillus ]
- Many strains are motile peritrichous flagella.
- coli are classified into four major group on basis of their pathogenicity :
a. Entero toxigenic E. coli
b. Entero invasive E. coli
c. Entero pathogenic E. coli
d. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
Transmission :
- Fecal contaminated feed and water
- Eggshell contamination at cloaca by excreta is also common with the bacteria present in the nest.
- A respiratory route may be involved due to contaminated dust in poultry houses.
- Ovarian route, with birds shading coli through uterine infection. Infected breeder hens transmit it to newly hatched chicks.
- Contaminated feed is a frequent cause of transmission
Pathogenesis :
Bacteria enter into birds through respiratory tract , skin trauma , cloaca , navel , etc
⬇
- coli can extend locally or gain access to bloodstream
⬇
Occurs coli septicaemia
⬇
Acute septicaemia to death
- Infection can also extend to serosal surfaces to cause subacute polyserositis and chronic granulomatous.
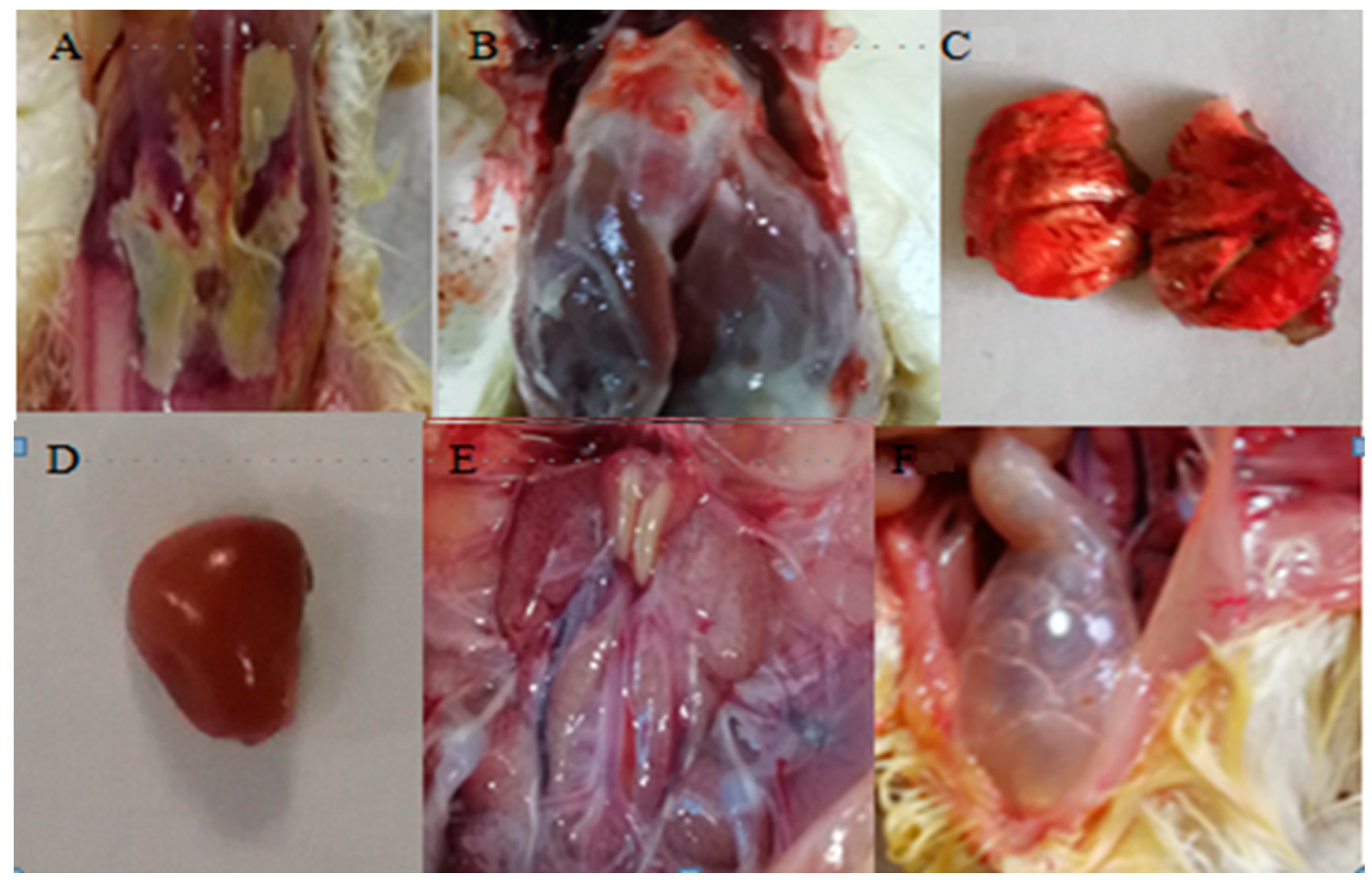
Major clinical and postmortem findings that are caused by E. coli :
- Colisepticemia
- Coligranuloma (Hjarre’s dis.)
- Air sac dis.
- Coliform cellulitis(inflammatory process)
- Swollen-head Syndrome (SHS)
- Coliform peritonitis
- Coliform Salpingitis
- Coliform osteomyelitis/synovitis
- Coliform panophthalmitis
- Coliform omphalitis/Yolk sac infection

Signs :
- Respiratory distress
- Reduced appetite
- Poor growth
- Decrease in production