Anaplasmosis in Cattle
Anaplasma marginale
Location and host
- Cattle are main host but infection also occurs in RBC of water buffalo, bison, African antelopes, Zebra, deer, mule, camel. Vector of this parasite are different species of tick ; Boophilus, Derma center, Hyalomma, Ixodes, Rhipicephalous but stable flies, tabonids and mosquitoes also transmit the disease.
Morphology
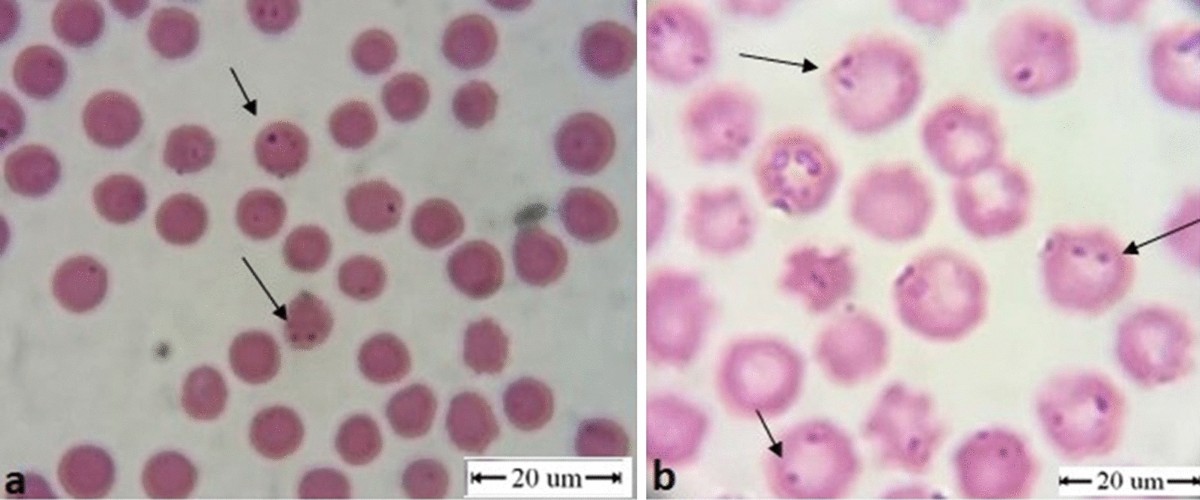
- A. marginale occur as round, filamentous, oval or disc like
- They are found near the margin of erythrocytes
- Size of parasite is 0.2-0.5µm in diameter.
- Only one organism is found in one red cell.
- In Giemsa-stained blood films, they are seen as round, small, dark red ‘inclusion bodies’ within red cells.
Life cycle : same as above.
Transmission
- Primary mode of transmission is through ixodid tick of genus Boophilus, Derma center, Hyalomma, Ixodes and Rhipicephalous.
- Argas and Ornithodorous also acts as vector.
- Mechanical transmission may occur through blood sucking flies; tabonid flies, stomoxys and mosquitoes.
- They can also be transmitted during surgical operations like dehorning, castration, vaccination , blood sampling, etc.
Clinical signs
- Incubation period is 15-36 days.
- Fever which fluctuates with irregular periods.
- Anorexia
- Pale/Jaundice mucous membrane
- Hemoglobinuria is absent
- In per acute cases, there is sudden onset of fever, anemia, icterus, severe dyspnea and death within 24 hours.
- In chronic case, there is severe anemia. Animal becomes susceptible to their infections.
- Loss of milk production in cows
- Abortion in pregnant cows.
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical signs and symptoms.
- Detection of organism in blood smears.
- Detection of organism by serological test to complete fixation, capillary tube agglutination, gel precipitation and fluorescent Ab tests.
Treatment
- Tetracycline @ 6-10 mg/kg body weight, single dose intramuscular (effective).
- Imidocarb and berenil are also used.
- Support and treatment include slow administration of blood transfusion.
Prevention and control
- Control of ticks: Dipping of animal on ectroparasiticidal solution helps in control of tick.
- Proper treatment of positive cases in segregation helps in effective control of disease.
A . centrale
Introduction
- These organisms are less pathogenic. All are same as marginale but they are commonly found in center of erythrocytes.
- Others same as above