Salivarian trypanosome
Sub- genus: Dutlonella
Trypanosomas vivax
- Disease produced by this parasite is known as ‘Nagana’. It produce chronic and acute type of Nagana in case of sheep, goat, cattle and transmitted mainly by ‘Glossina morsitans’.
Location and host
- This parasite is found in blood of cattle, sheep, goat, horses, camel. These are transmitted by tse-tse flies of Glossina sps.
Morphology
- vivax is monomorphic, ranging in size from 20-27 µm.
- Undulating membrane is inconspicuous.
- Kinetoplast is large and terminal.
- Posterior end is broad and rounded
- Short free flagellum is present
- In fresh blood fils, vivax moves rapidly across the microscopic field.

Life cycle
- Infection acquires by host when flies inoculate intermediate metacyclic trypanosome during feeding
- These intermediate form changes to trypomastogote
- Multiplies through binary fission and change into stumpy form
- These short stumpy forms are taken up by vector
- Development occurs in proboscis. Intermediate changes into trypomastigote
- Trypomastigote multiplies by binary fission and change into epimastigote form
- Epimastigote then changes into metacyclic infective trypanosome
- Pass to hypopharynx and cycle repeats.
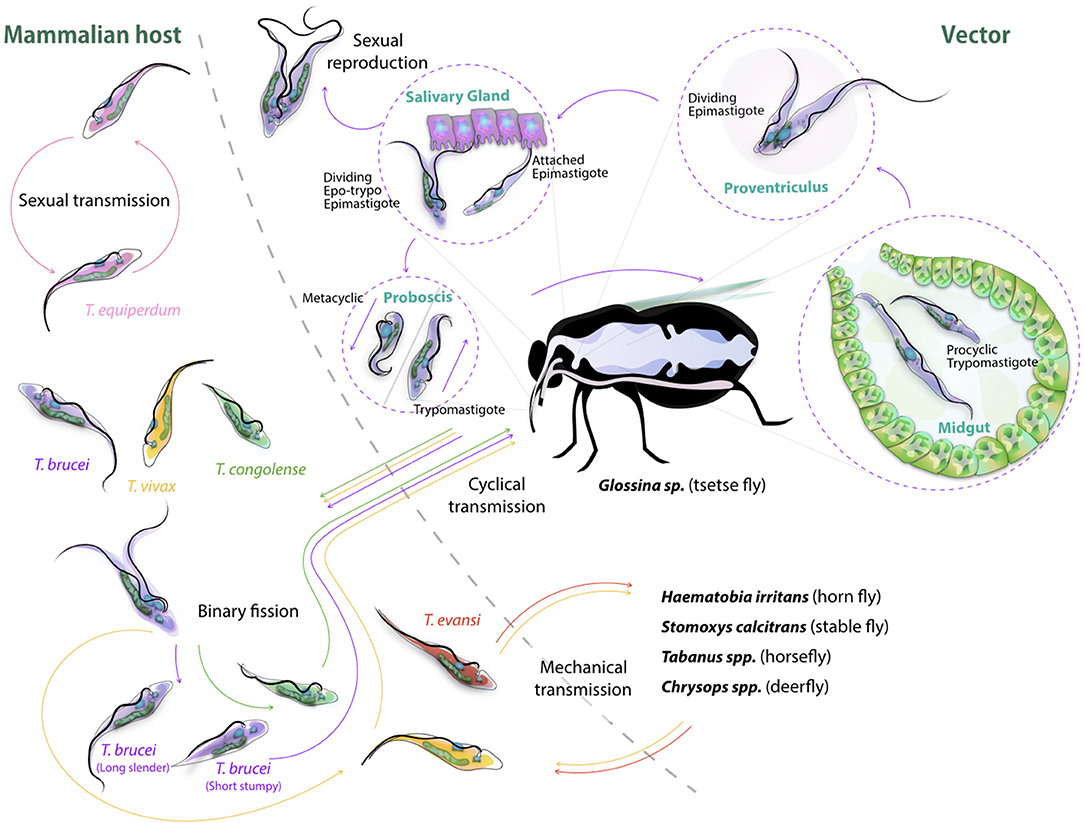
Mode of transmission
- Transmission is mainly through inoculation of infective stage to blood by vector.
Pathogenesis/ Clinical signs
- Most important in cattle, strains of vivax in west Africa are more pathogenic than ones in East Africa.
- Causes acute hemorrhagic disease
- Shows unspecific signs such as fever, anorexia, weight loss, reduced milk yield, enlarged lymph nodes, abortion, diarrhea, anemia, leukopenia and eventual leukocytes.
Diagnosis
- Demonstration of parasite in blood smears.
Treatment
- Diminazene aceturate @ 3-10 mg/kg, intramuscular.
- Isometamidium @ 0.25-1 mg/kg intramuscular.
- Nomidium bromide / Homidium chloride @ 1 mg/kg, sub-cutaneous.
- Pyrithidium bromide @ 2-2.5 mg/kg.
Control
- Use of fly repellants and insecticides
- Control of breeding of insects vectors.