Remote sensing
- Remote sensing is to collect data and information about an object or event without any physical contact with that object or event.
- Remote sending is a phenomenon that has many applications including geology, surveying, forestry, photography and many more.
- But in the field of agriculture, remote sensing has found significant use.
- There are many applications of remote sensing in the agricultural sector
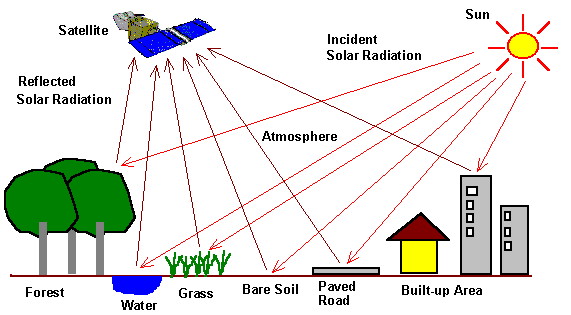
Examples:
The nature of the object i.e. green trees has a reflection of sunlight from vegetation which will provide information on the reflection of coefficient of that object and its spectral variation.
Below are some concepts where we can use GIS applications:
a. Forecasting of Crop production:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can predict the expected crop yield and production in agricultural land and we also can estimate about the quantity of crops under specific situations
b. Crop progress and crop damage Assessment:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can determine the penetration of land. A ratio of crop that has been damaged and progress of crops, left in farmlands.
c. Analysis of Cropping Systems and horticulture:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can study the planting system of various crops.
- These technologies can also be used for flower growth in the industry of horticulture.
- By which we can analyze the pattern of flower growth and predict with the help of various analyses.
d. Identification of Crop:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can identify crops. If our crops show some strange characteristics, then need to observe our crop. Further, the collected data has been taken to labs where on different aspects of crop and the culture of crop study.
e. Estimation of crop acreage:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can estimate agricultural land where we can plant our crop.
- It is usually a large procedure if we do it manually, due to the huge sizes of agricultural lands that need to be estimated
f. Assessment of crop condition and stress detection:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can assess the crop health condition and assess the stress of crops. Further, these data can be used to calculate the quality of the crop
g. Identification of harvesting and planting dates:
- By using remote sensing technology, now farmers can notice a wide variety of components which includes types of soil and weather patterns to forecast the harvesting and planting dates or seasons of each crop.
h. Estimation and modeling of crop yield:
- By using remote sensing technology, experts and farmers can predict the expected yield of the crop for agricultural land by analyzing the crop quality and the area of that land.
i. Identification of disease and pest’s infection:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can identify the pests in agricultural land and provide data on correct mechanism to control pests. So that we can get rid of this disease and pests on the land.
j. Estimation of soil moisture:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can measure soil moisture.
- With the help of these technologies, we can get soil moisture data that will help us in determining the moisture quantity in soil and estimates about the crop type that can be sown in that soil.
k. Irrigation management and monitoring:
- As we know we can get soil moisture information by using remote sensing technology.
- On the other sides, this extracted information can also be used in determining the deficiency in soil moisture and we also can plan if soil needs irrigation or not
l. Mapping of Soil:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can map our soil as it plays an important role.
- With this technology, farmers can get to know what type of soils are good for which crop type and which soil needs irrigation and which one does not need to be. This provided information also helps us in precision agriculture.
m. Drought Monitoring:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can monitor the patterns of weather and drought patterns for a given agricultural land.
- Further this information can be used to predict the rainfall patterns for an area and told us the time difference between the current rainfall and next rainfall that helps us to keep drought record.
n. Mapping of land cover and land degradation:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can design the land cover for a particular area. With this data experts can predict which land area has been degraded and which area are still in good condition.
- It also helps them for measures curb land degradation during its implementation
o. Problematic soil identification:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can identify the soil problems, while sustaining in the planting season for optimum crop yield.
p. Detection of Crop nutrient deficiency:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can help experts and farmers to determine the proportions of deficiency of crop nutrients and provide treatments that helps to increase the level of nutrients in crops, so that we can increase crop yield.
q. Reflectance modeling:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can extract information about the reflectance of the crop, and it is the only technology that provides this information.
- This reflectance of crop is depending upon the amount of moisture present in soil and nutrients in the crop, that have a significant effect on crop yield
r. Determination of water content of field crops:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can determine the moisture content of soil and estimation of content of water in crop
s. Forecast of Crop yield:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can estimate accurately about the expected yield of the crop during planting season with the help of various crop information such as crop and soil moisture level, crop quality, and crop land cover.
- Further combining all this data, we can estimate accurately crop yield.
t. Flood monitoring and mapping:
- By using remote sensing technology, agricultural experts and farmers can map out the areas that are hit by floods and areas having poor drainage functions.
- With the help of this data, we can prevent any future flood disaster
u. Collection of current and past weather data:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can collect and store, current and past data of weather that can be used for prediction and future decision making.
v. Crop intensification:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can collect important crop data such as crop rotation, crop pattern and crop diversity for a particular soil of land.
w. Mapping of water resources:
- By using remote sensing technology, we can it for mapping water resources for agricultural land.
- With the help of such technology farmers can get to know about the availability of water resources and the adequacy for farmlands.