Types of Aquaponics
Aquaponics integrates aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (soilless plant culture) in a symbiotic system. Different designs are adopted based on space, crops, fish species, and resource availability.
a. Media-Based Aquaponics (Flood and Drain System)
- Plants are grown in a media bed (gravel, expanded clay, and perlite).
- Nutrient-rich fish water is cycled through the media, which acts as a bio filter.
- Water drains back into the fish tank after filtering.

Advantages:
- Simple and low-cost; suitable for small-scale use.
- Media acts as both plant support and bio filtration system.
- Easy to manage for beginners.
Disadvantages:
- Not efficient for large-scale commercial farming.
- Media can clog over time, requiring cleaning.
b. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)-Based Aquaponics
- Water from the fish tank flows as a thin film through sloping channels.
- Plant roots absorb nutrients directly from flowing water.
Advantages:
- Requires less water compared to media systems.
- Plants have direct and continuous access to nutrients.
- Suitable for leafy greens and herbs.
Disadvantages:
- Roots can suffer from oxygen deficiency if water stops flowing.
- System failures (pump breakdown, power cut) can quickly damage plants.

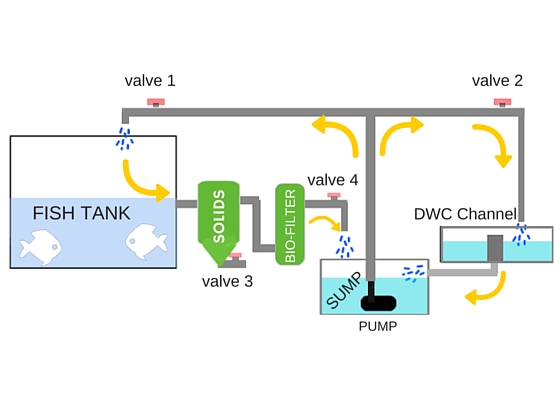
c. Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Raft System
- Plants are grown on floating rafts with roots suspended directly in nutrient-rich fish water.
- Air stones or diffusers provide oxygen to roots.
Advantages:
- Good for commercial-scale production.
- Steady nutrient availability ensures fast growth.
- Works well for leafy vegetables like lettuce, spinach, and basil.
Disadvantages:
- Requires continuous aeration; energy-dependent.
- Roots are prone to pathogens if water quality is poor.

d. Vertical Aquaponics
- Plants are grown in vertical towers or stacked layers.
- Fish water is pumped to the top and trickles down through plant roots.
Advantages:
- Space-saving; ideal for urban and rooftop farming.
- Higher plant density per unit area.
- Visually attractive for commercial marketing.
Disadvantages:
- Higher installation cost.
- Limited to small and lightweight crops like herbs and leafy greens.

f. Hybrid Systems
- Combination of two or more systems (e.g., media bed + NFT or DWC).
- Provides flexibility to grow different types of crops.
Advantages:
- Better nutrient and space utilization.
- Can optimize for both leafy vegetables and fruiting crops.
Disadvantages:
- More complex to design and manage.
- Higher monitoring and labor requirements.