Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- RNA is synthesized in nucleus but is formed in the nucleolus, etc. It helps in protein synthesis.
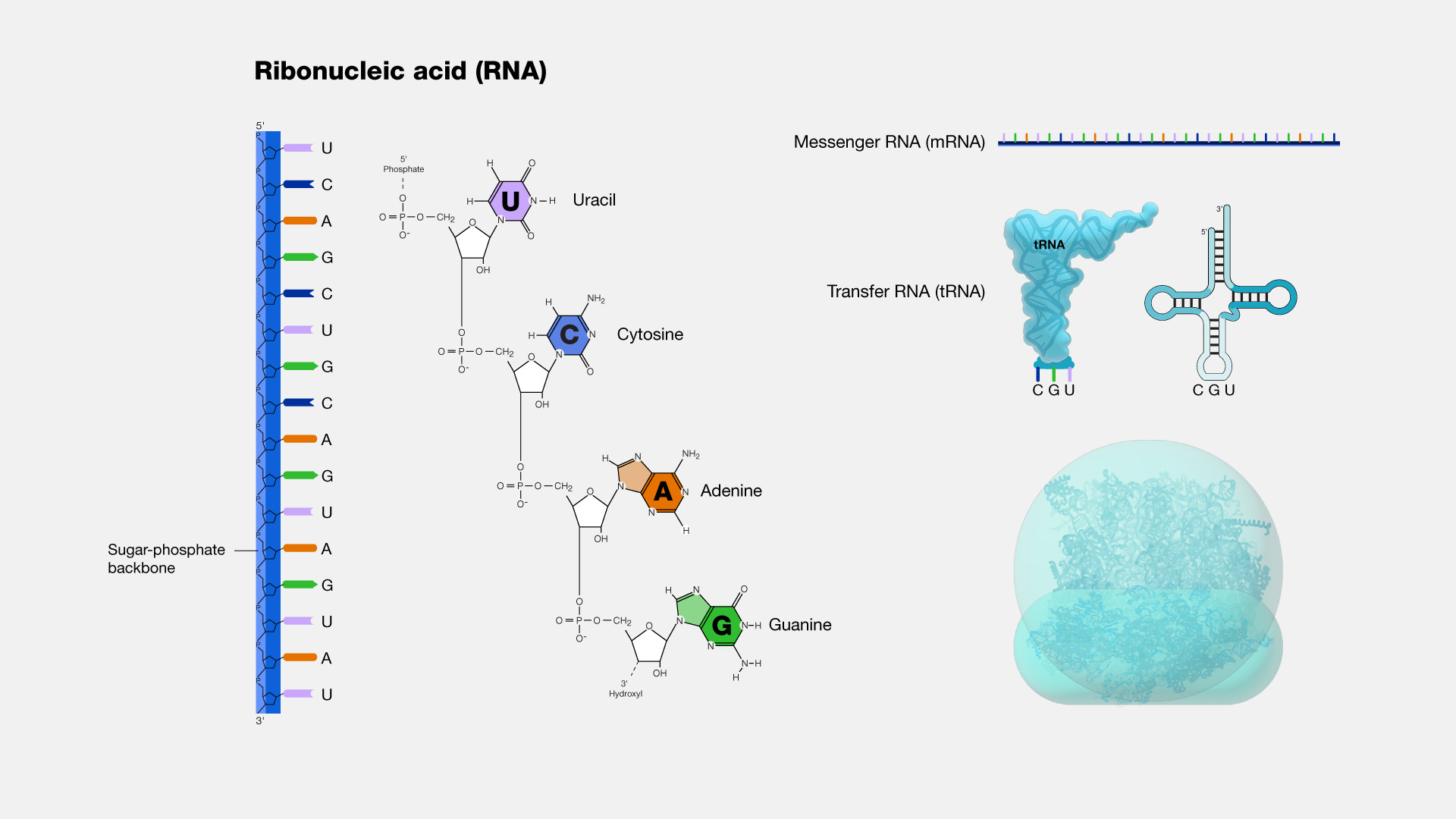
Structure
- Like DNA, RNA is a macromolecule but comparatively smaller than DNA.
- It is single stranded , formed of polynucleotide chain.
- RNA like DNA is formed of several hundred or thousands of nucleotides arranged in a linear sequence and connected together by 3’-5’ phosphodiester bonds.
- Each nucleotide consists of a ribose sugar, phosphate and one of the four nitrogen bases.
Nucleotides of RNA are called ribonucleotide.
- The nitrogen bases in RNA are adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and uracil. (Thymine of DNA is substituted by uracil of RNA).
RNA is long unbranched polynucleotide molecule, made up of Single chain. It is non-heredity nucleic acid except in virus. It is polymer of nucleotides made up of pentose ribose sugar, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous bases(Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil). Ribose sugar form backbone along with phosphoric acid for the attachment of nitrogenous bases. Nitrogenous bases joint to ribose sugar by glycosidic bond. RNA is found in nucleus, ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplast and cytoplasm.