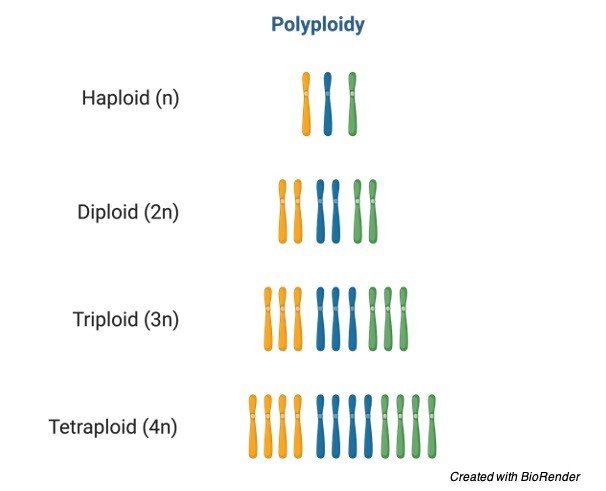
Polyploidy:
The organism with more than two sets of chromosomes are called polyploids which are of different types;
1.An organism with three sets of chromosomes is called triploid.
2.An organism with three sets of chromosomes is called tetraploid.
3.An organism with three sets of chromosomes is called pentaploid.
4.An organism with three sets of chromosomes is called hexaploid.
Causes of polyploidy:
- It may arise naturally or artificially as a result of increase in number of chromosomes sets.
- If cytoplasm fails to cleave, a tetraploid is formed.
- A fusion of a diploid and haploid gametes results into triploid organism while the fusion of two diploid gametes produces a tetraploid individual and also it may occur if an egg is fertilized by more than one male gametes.
- Autoployploidy induced artificially by
- Chemicals by colchicine,
- Radioactive substances.
- Alternate heat and cold shocks.
Types of polyploidy:
It is of two types:
a. Autoployploidy:
They are those polyploids which are derived from the multiplication of chromosomes within the same species.
b. Allopolyploidy:
They are those polyploids which are formed due to the doubling of chromosomes number in a hybrid.
Role of polyploidy:
1.They help in evolution of new varieties, species and genera.
2.They often associated with advantages features like increased size, hardness and resistance to disease.
3.Seedles varieties of watermelons, tomatoes, grapes, etc. have been produced by triploids.
4.Disease resistant and high yielding species of crops are produced by allopolyploidy.
5.Polyploidy is usually used in obtaining fodder plants.
6.Polyploid plant often faces the ecological hazards more boldly.