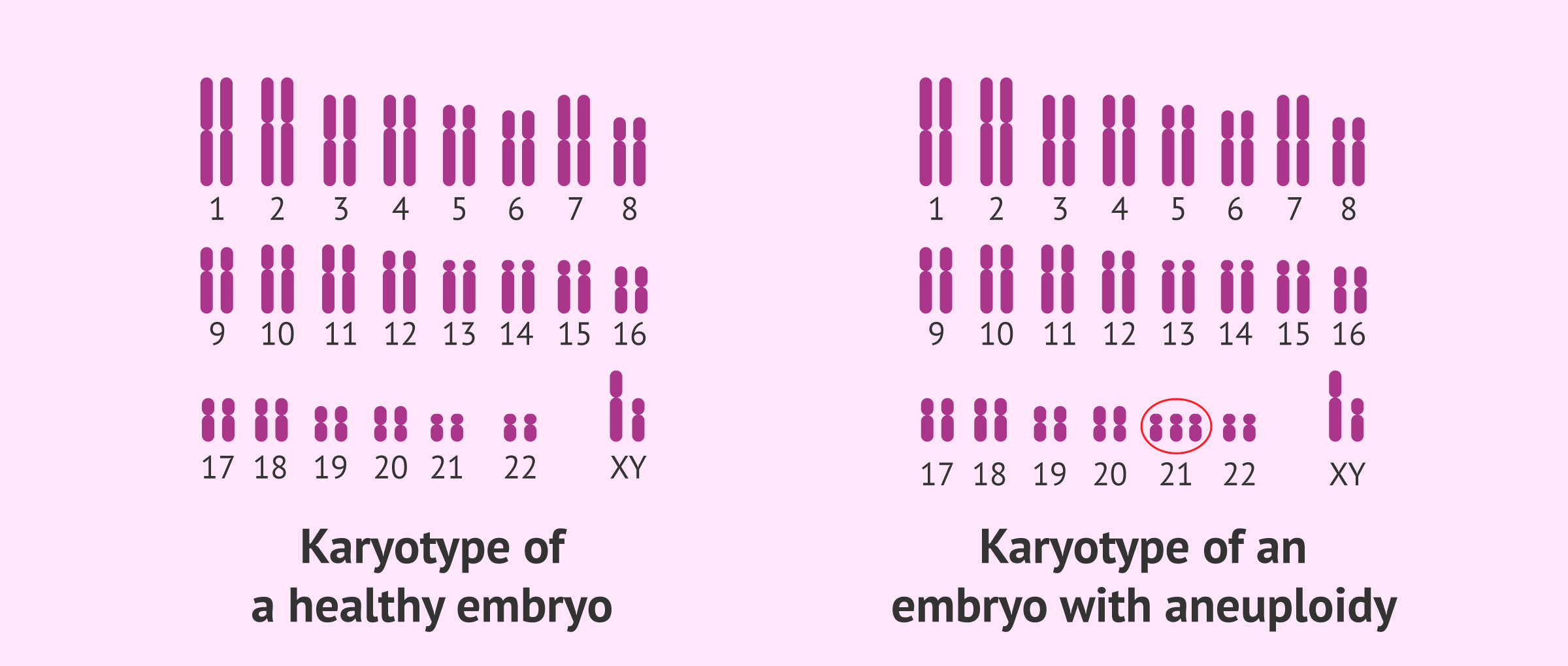
Aneuploidy
- Refers to one or few chromosomes extra or missing from 2n.
- It is of following types:
i) Nullisomic: One chromosome pair missing (2n+/-)
ii) Monosomic: One chromosome missing (2n-2)
iii) Double monosomic: One chromosome from each of two different pairs missing.(2n-1-1)
iv) Trisomic: One chromosome extra (2n+1)
v) Tetrasomic: One chromosome pair extra (2n+2)
Uses of Aneuploids
- Used to determine the phenotypic effects of loss or gain of different chromosome.
- Useful in production of substitution lines.
- Useful in identifying chromosomes involved in translocation.
- Locating a linkage group and a gene to a particular chromosome.
- Produce alien addition and alien substitution which are useful in gene transfer from one species to another.
Production of Aneuploids
- From autotriploid plants
- Progeny from a cross between tetrasomic (2n+2) and diasomic (2n) plants.
- A synaptic and desynaptic plants.
- From translocation heterozygoytes.