Introduction
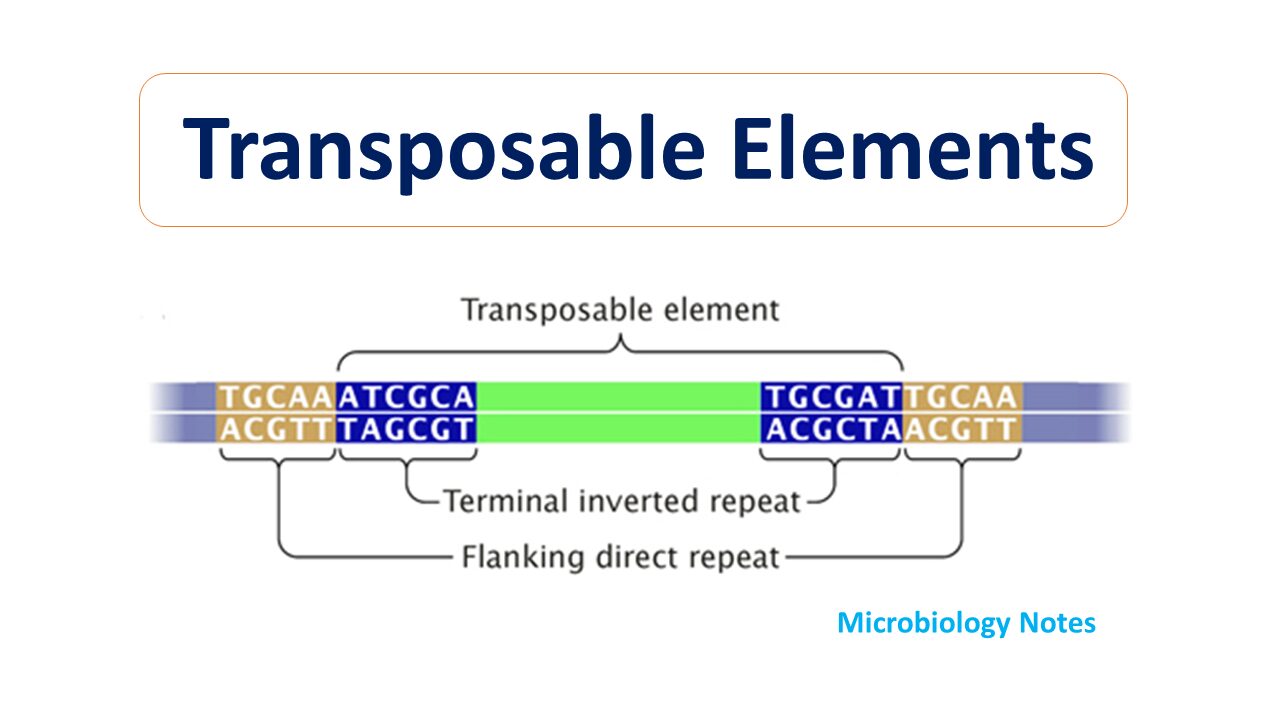
- A transposable element (TE, transposon, or jumping gene) is a DNA sequence that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell’s genetic identity and genome size.
- Transposition often results in duplication of the same genetic material.
Types of transposable genetic elements
a) Insertion sequence:
- It is a mobile piece of DNA that is capable of inactivating a gene into which it inserts.
- They are believed to be responsible for spontaneous gene mutation in bacteria and bacteriophage.
- When this insertion sequence transposes, this direct repeat remain at the site of insertion in the host chromosome.
- It can be explained as:
b) Transposons:
- It is a DNA Segment capable of changing its location within or between the chromosome.
- They are usually 2000 bp long and carry one or more genes unrelated to their transposability.
- The general events can be shown below:
Ac and Ds element in maize
- Discovered by Mc clintock.
- Responsible for stripping and spotting of maize kernals.