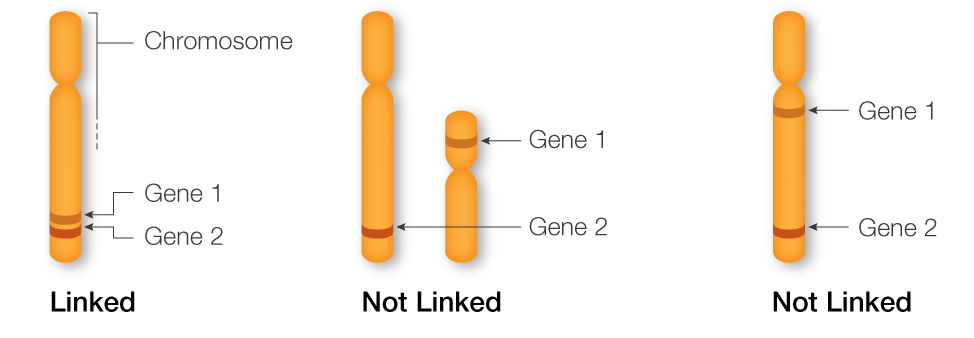
Linkage
- Linkage is the close association of genes or other DNA sequences on the same chromosome.
- The closer two genes are to each other on the chromosome, the greater the probability that they will be inherited together.
Types of linkage
A. Depending on absence or presence of recombinant phenotype:
a) Complete linkage
- The genes located on the same chromosome do not separate and are inherited together over the generations due to the absence of crossing over.
- Complete linkage allows the combination of parental traits to be inherited as such.
- It is rare but has been reported in male Drosophila and some other heterogametic organisms.

b) Incomplete linkage
- Genes present in the same chromosome have a tendency to separate due to crossing over and hence produce recombinant progeny besides the parental type.
- The number of recombinant individuals is usually less than the number expected in independent assortment.

B. Depending on whether all or some dominant and some recessive genes are linked together:
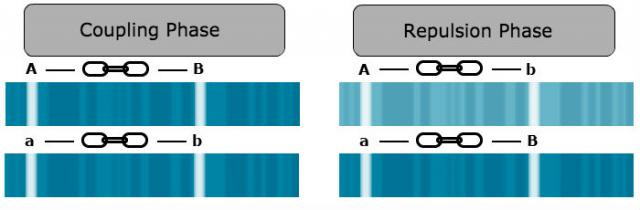
i) Coupling phase of linkage: Dominant alleles of the linked genes are present in the same chromosome. Eg: Colored full/ color less sunken genes in maize.
ii) Repulsive phase of linkage: Dominant alleles of some genes and recessive alleles of other gene are present in the same chromosome. Eh: Colored shrunken/ color less full genes in maize.