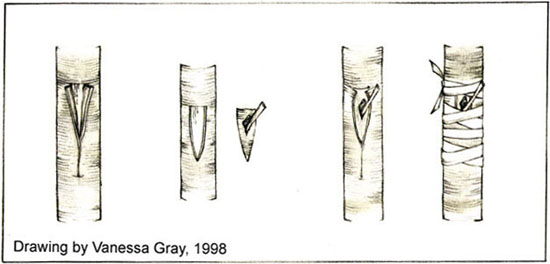
Shield Budding:
- This is the methods of budding in which a single bud with a little wood or without wood is taken but from the scion plant and is given a shape of ‘shield‘ before it is inserted into the root stock
- It is done in following three ways:
A. Shield Budding by T method:
i) Selection of Bud Wood or Bud Stock:
- Fairly well matured, round bud stick of pencil thickness and of past season’s growth, brownish color, having dormant plumy buds is selected from the desired tree
- The leaves are removed from the bud to avoid injuries to the axillary buds
ii) Selection of Stock Plant:
- Vigorous growing root stock seedling with pencil thickness having height of about 1 1⁄2 to 2 feet is selected
- The seedling should be in free sap flowing condition
iii) Removal of Bark from the Stock Plant:
- On selected seedling ( root stock ) at the height of about ( 1 1⁄2 inches to 2 inches from ground level ) vertical cut followed by a horizontal cut across the top at right angle is made carefully with budding knife
- The cuts may be depending upon the wood
iv) Removal of Bud:
- From the selected bud stick a plumy bud is taken out carefully with wood by taking 1⁄2 inch below the bud
- The wood is then removed from the bud along with portion of bark is given a shape like shield
V) Inserting the Bud:
- The flaps of bark on either sides of the cut on the stock plant are loosened with very portion of budding knife
- And kept ready to receive bud
- The bud is then inserted from the top of the cut and pushed downward beneath the bark, and is held in position
vi) Bandaging :
- To bring about a firm cambial contact, the operated portion is tied with polythene strip keeping the growing point of bud exposed
- Under the normal condition union taken in about 5 weeks
- After the successful union, the bud sprouts or new shoots comes out and bud grows vigorously
- The portion of stalk above the union is then cut off step by step and bandage is removed
- When the new shoots develop at its vigorous and the bud graft is hardened in the nursery for 6 to 8 months, it becomes ready for permanent plantation
B) Shield Budding by ‘I’ Method:
- It is adopted where a great deal of rains occur
- Water running down the stem of the root stock
- After in case of the ‘ T’ cut soaks under the bud and causes decay of the shield piece of bud
- Under such condition and ‘inverted’ T budding may give better results, since it is more likely to the below the bark inform running water
- The technique required in this method is same as that in T method except that the incision on the stock has the transceivers ( cross ) is taken on root stock and it is bent so that the bark become loose
- Then the bud is inserted and tied firmly with plastic tape
C) Simple Shield Budding by Insertion Method:
- A simple length wise incision ( cut ) is taken on root stock and it is bent so that the bark become loose
- Then the bud is inserted and tied firmly with plastic tape.
- Union takes place within two to three weeks
- Union takes place within two to three weeks

II) Patch Budding: (Mango):
- Patch budding is somewhat slower and more difficult to perform than T budding
- But is widely and successfully used on the plants which got thick bark
- The patch of bark is removed from the stem of the root stock
- Then the patch of bud of exactly the same size is removed from the bud stock taken from desired tree
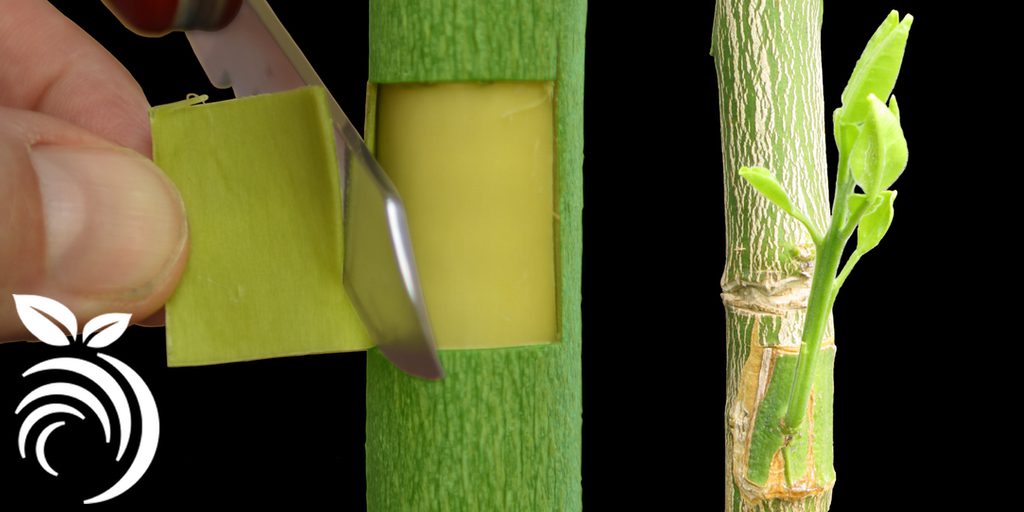

- Polythene film is tied to protect same
- Separating and October are considerable to rather most suitable months for patch budding in mango
III) Flute Budding:
- This method makes use of the ring of tissues adjoin the bud relatively thick barked tree thicker than 1 cm. and in active stage of are commonly budded by this method
- It is successfully used in Ber and Cashewnunt trees
- On the bark of root stock two horizontal cuts about ‘1 1⁄2 to 2’ apart are made to the extent of about 3/ 4 of the diameter of the stem
- Vertical cuts connecting the horizontals cuts at both the ends are mode and semicircular bark is removed
- The scion is prepared by repeating the same methods on the bud stack and the bud accompanying with flute of bark is placed against the corresponding cut portion of the stock
- After this typing is attended in usual ways
- All other operation is also similar to those in shield budding

IV) Ring Budding:
- The nature and method rendered its usefulness only to small stocks
- This is more or less an extension of flute method
- Budding operation is performed when the plant is in sap flowing condition
- A complete ring of bark is removed around the stem of the stock in order to from matrix
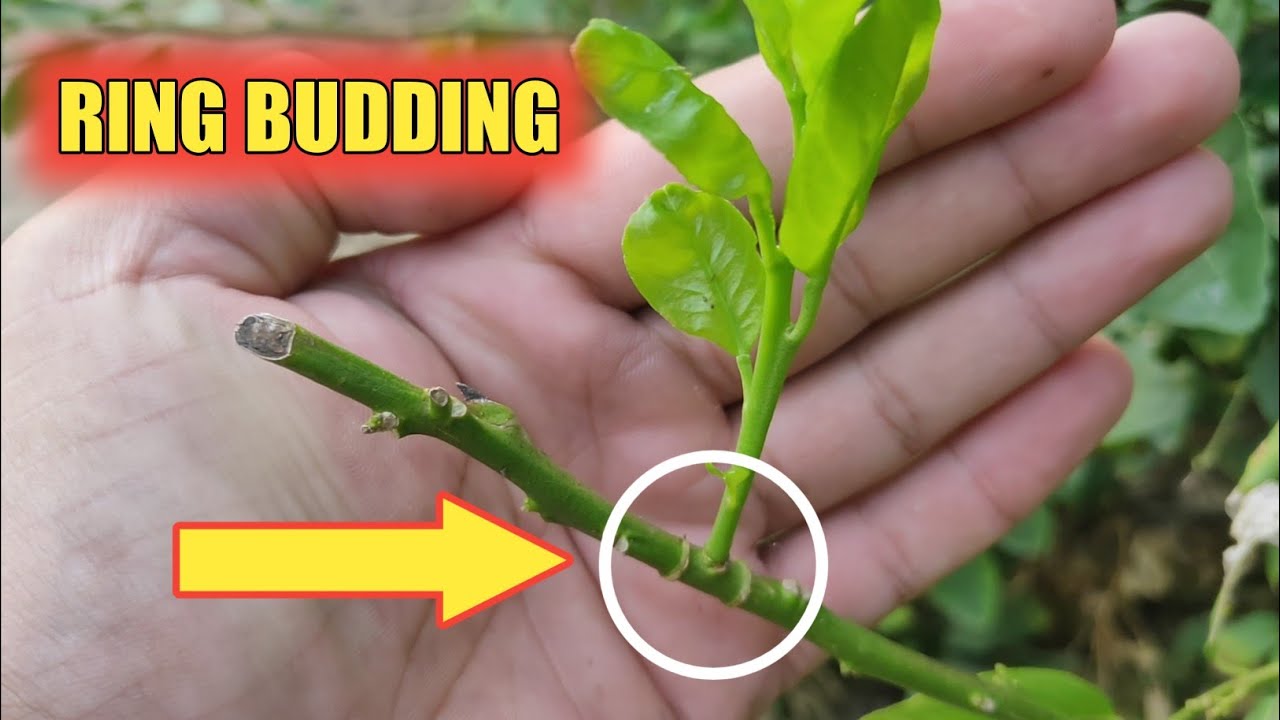

- A complete ring of bark of the same with a prominent, plumy, healthy bud is removed from bud stick when placed on stock; it extends all around the stock
- After placing the ring in position typing is done in usual manner, failure of the bud to unite, result in loss of terminal portion of stock above the ringed portion