Bulk Method
- Inbreed in bulk to have homozygous lines
- Select superior lines after F6
- Crosses with no high heritability traits segregating
Points to consider in Bulk Method
- Natural selection changes gene freq. via natural survival
- Breeder may assist nature and discard obviously poor types
- Relieves breeder of most record keeping
- Most of us treat bulks with extremely low inputs and low expectations.
Note:
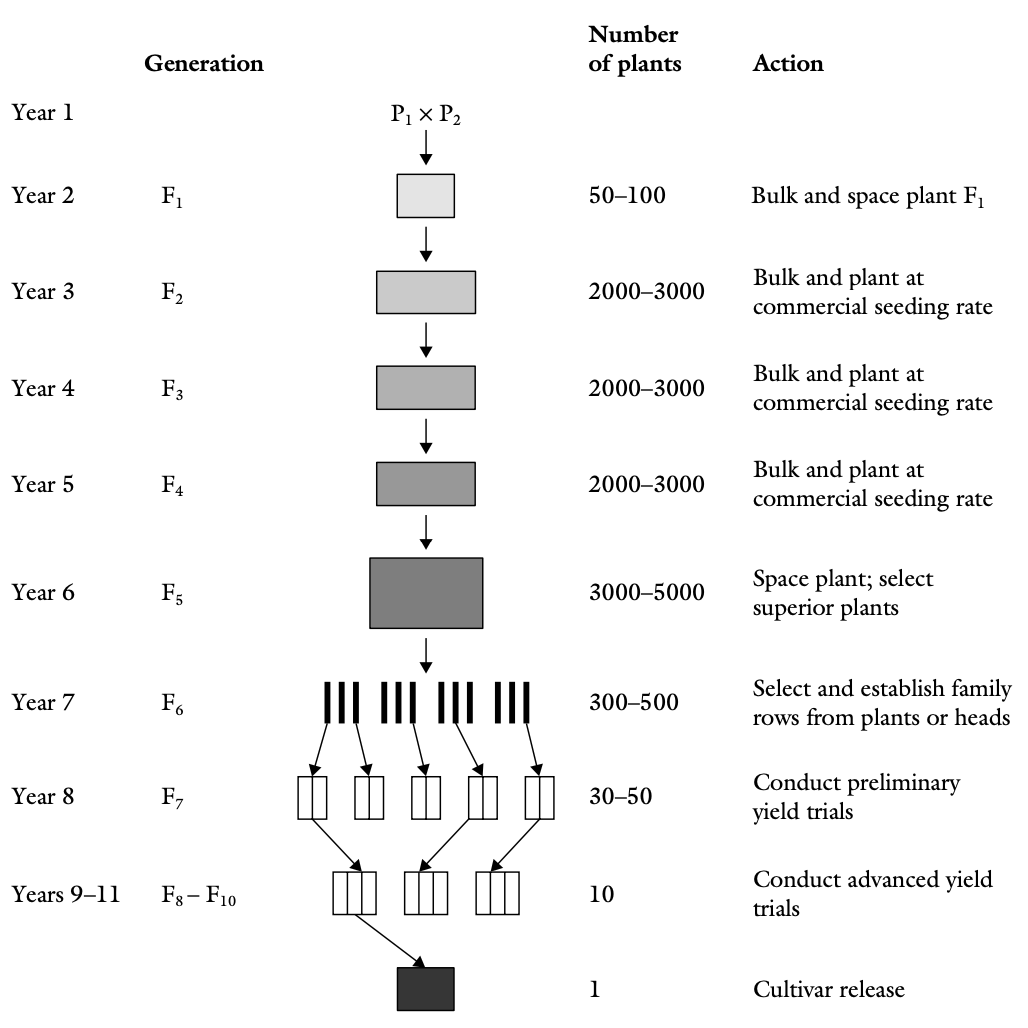
- The bulk method is a procedure for inbreeding a segregating population until a desired level of homozygosity is reached.
- Seed used to grow each selfed generation is a sample of the seed harvested in bulk from the previous generation.
- In the bulk method, seeds harvested in the F1 through F4 generations are bulked without selection; selection is delayed until advanced generations (F5-F8).
- By this time, most segregation has stopped.
Advantages of Bulk Method
- Less record keeping than pedigree
- Inexpensive
- Easy to handle more crosses
- Natural selection is primarily for competitive ability
- More useful than pedigree method with lower h2 traits
- Large numbers of genotypes can be maintained
- Works well with unadopted germplasm
- Can be carried on for many years with little effort by the breeder
Disadvantages of Bulk Method
- Environmental changes from season to season so adaptive advantages shift
- Most grow bulk seed lots in area of adaptation
- Less efficient than pedigree method on highly heritable traits (because can purge non-selections in early generations)
- Not useful in selecting plant types at a competitive disadvantage (dwarf types)
- Final genotypes may be able to withstand environmental stress, but may not be highest yielding
- If used with a cross pollinated species, inbreeding depression may be a problem