Graphical Properties of variable and fixed costs
a) TVC: inverse S-shape: so follow the law of variable proportion. It means at the initial stage of production, productivity increases as more variable factors used and average variable cost falls.

b) TFC: Straight line parallel To the output axis

Fig:1 TFC

Fig: 2 TVC

Fig: 3 TFC, TVC, TC
Average total cost (ATC) or Average cost – total cost per unit of output (AC=TC/ y= AFC+AVC).
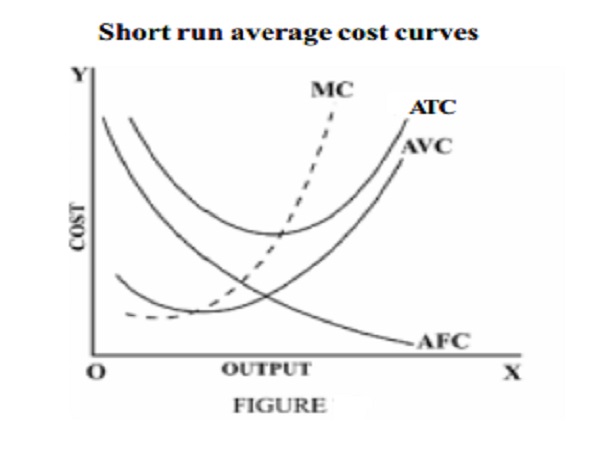
Fig: Graph of SATC
Total fixed cost (TFC)
Cost which doesn’t change with changes in the quantity of output. These costs are buying tractor, irrigation pipe, or simple plow having durable use. Mathematically,
TFC= Unit of fixed factors X price of the factor.

Average fixed cost (AFC)
Total fixed cost/quantity of output (Kg or quintal) i.e. AFC=TFC/y
.webp)
Fig: Graph of Average Fixed cost
Total variable cost (TVC)
Sum of amounts spent for each of the variable inputs used.

Average variable cost (AVC)
Total variable cost by dividing the quantity of output ( i.e. AVC=TVC/y)
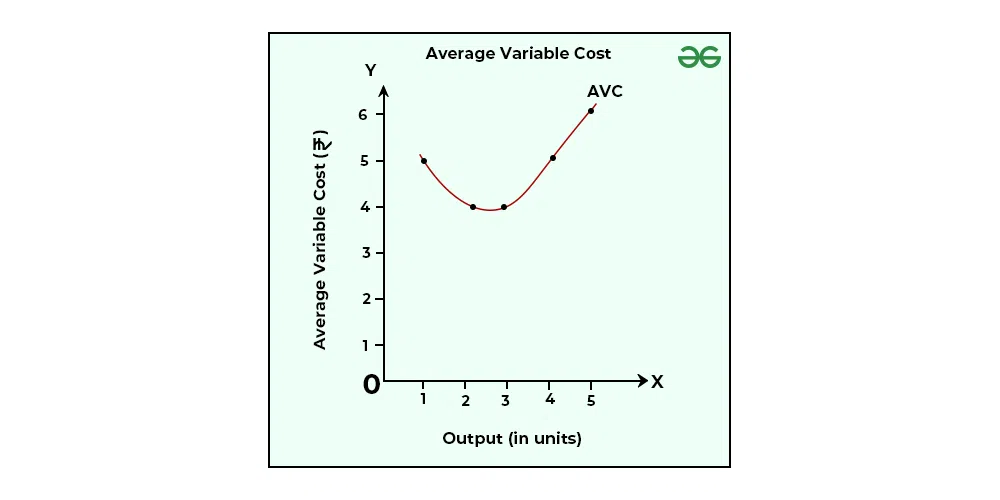
Fig: Graph of Average Variable Cost
Marginal cost
Marginal cost is the addition made to the total cost by the production of one more unit of output. According to Dooley, MC is the change in total cost associated with the change in output;
i.e, MC = (change in total cost)/(change in output)
.webp)
Mathematically, TC is the first derivative of the TC function: MC=δC/ δX
Graphically, MC is the slope of the TC curve. MC curve follow U shape.
Relation: When AC falls, MC is less than AC, AC rises, MC is greater than AC, MC cut AC at its lowest point.
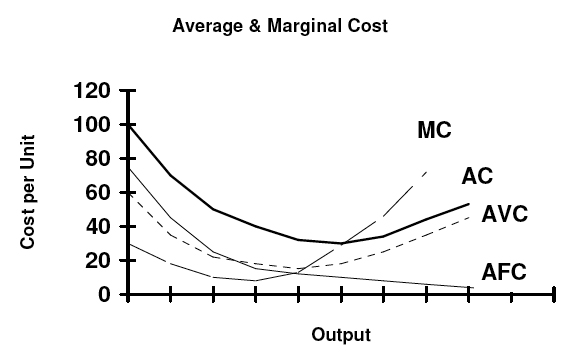
Fig: MC with AC VC and FC
Total Revenue / Marginal revenue
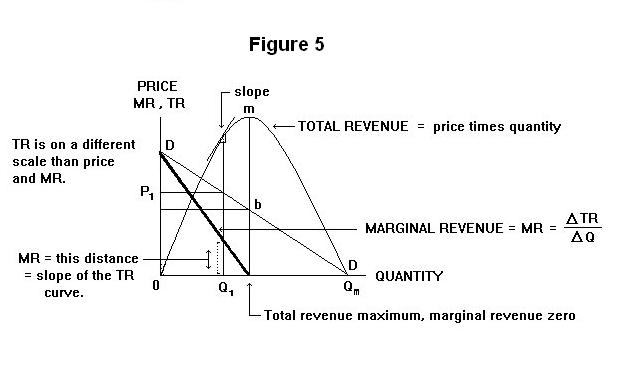
a) Total revenue: The firm gets from the sale of its products
Revenue = price X output
Average revenue: (Total revenue) / (total output)
i.e AR = Price
b) Marginal revenue: it is an addition made to total revenue by the sale of an additional unit of the product in the market Fig: equation of MR
Efficient Production
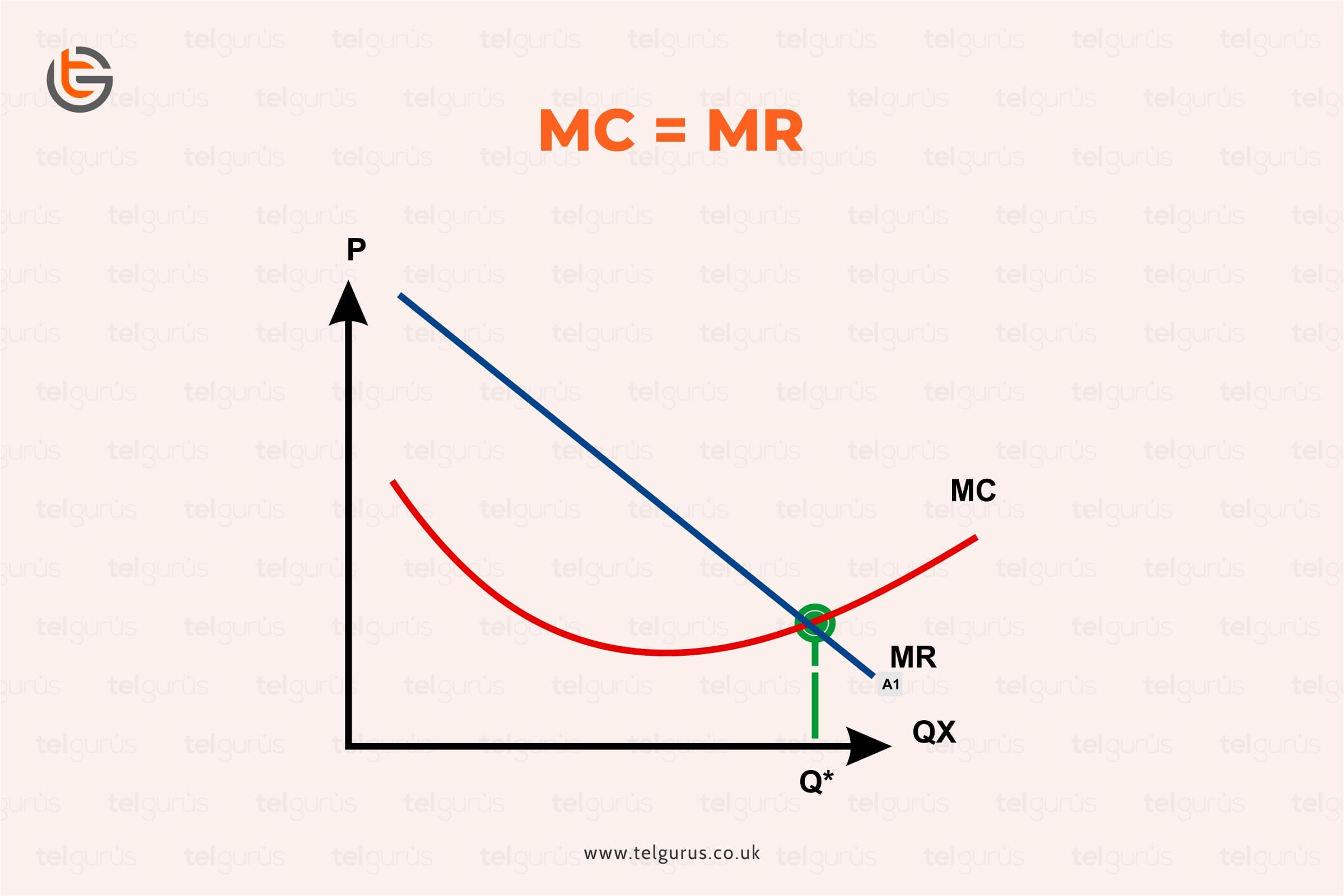
The MC=MR is optimizing rule force adjustments in output because of inequalities in cost and returns at the margin. If MR is at any level of output is exceeds MC, that inequality simply tells the operator that an additional surplus can be captured and added to profit by increasing outputs. The opposite signal is forceful when MC exceeds MR.