Blue Tongue (BT)
Syn: Sore mouth, sore muzzle, ovine catarrhal fever, Pseudo FMD, Stiff lamb disease
- It is infectious non-contagious arthropod borne virus disease of domestic and wild animals.
- It is characterized by inflammation of mucus membrane, congestion, swelling, rhinitis and inflammation of coronary band of foot.
- This is predominantly a disease of sheep but occasionally cattle and goats are affected.
- In cattle, disease mostly remain in sub-clinical form.

Etiology
- Orbivirus of Reoviridae family
- Virus persist for long period in meat and offal and killed by 3% NaOH
- Virus can persist for a long time in meat and blood. It can thrive even upto 7 years in stored chick embryo kept at 6°C.
- Virus is 65-80 nm in diameter, RNA virus
Epidemiology
- BTV spreads through species of Culicoides insects.
- Onset of monsoon spreads the disease.
- Disease is distributed worldwide, with outbreaks occurring in various regions including Europe, Asia, Africa and Americas.
- Mortality ranges from 2-90%.
Transmission
- Culicoides midges’ bites
- No transmission by direct and indirect contact
- Rarely virus in semen and contaminated semen may infect recipient cows.
- Blood also act as infective materials.
- Vertical transmission in cattle
Pathogenesis:
- Following entry of virus, they multiply in blood stream leading to primary viremia.
- Virus then localizes in endothelial lining of blood vessel
- Virus gets attached with RBCs. Characteristic lesion appears due to destruction of blood vessels.
Clinical Findings:
Incubation period of disease ranges from 1-10 days
Sheep:
- Fever around 106°F that lasts for 1-2 days
- Loss of body condition, emaciation, loss of wool in severely affected ones
- Inflammation, ulcers and necrosis in around mouth, i.e. gums, cheeks, tongue
- Edematous lips, dental pads, face, ears, mandibular space
- Tongue becomes cyanotic/bluish/purplish blue and lenticular shaped ulcers appears in tongue
- Frothy salivation, nasal discharge
- Reddening of coronary band causing lameness
- Abortion and congenital malformation
- Anorexic and increased respiration
- Death may occur due to aspiration pneumonia

Cattle:
- Sub-clinical stage and remain source of infection for sheep
- Fever, salivation, congestion, swelling and ulcers inside mouth
- Hydrocephaly in calves
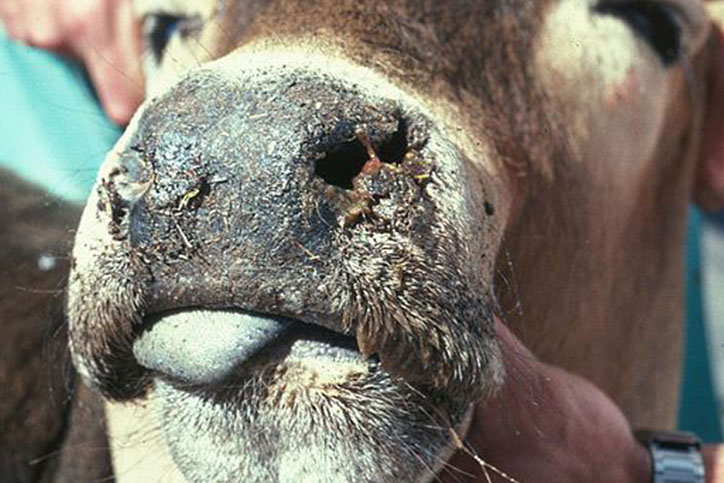
PM Findings:
- Small, hyperemia, edema, cyanosis and skin thickening
- Petechiation, erosion and ulceration of buccal mucosa
- Edema of skeletal and cardiac muscles of heart
- Swelling and necrosis of muscles with enlarged LN
- Hyperemia and edema of abomasal mucosa
- Swelling and congestion of spleen and liver
- Hemorrhage in coronary band

Diagnosis:
- Based on clinical findings
- Based on PM findings
- Hematological examination: Leukopenia
- Serological test: CFT, ELISA, AGDT, VNT, FAT
- Animal inoculation test: Suspected blood or tissue suspension is used at height of temperature for inoculation.
- Isolation of virus in chicken embryo cell
Differential Diagnosis:
- FMD:
- Highly contagious disease and spread by direct contact
- Absence of cyanotic changes in tongue
- Pink line appears on coronet in blue tongue which is absent in FMD
- No pneumonia

- MCF:
- Extensive erosion in buccal cavity, tongue, hard palate
- Presence of corneal opacity

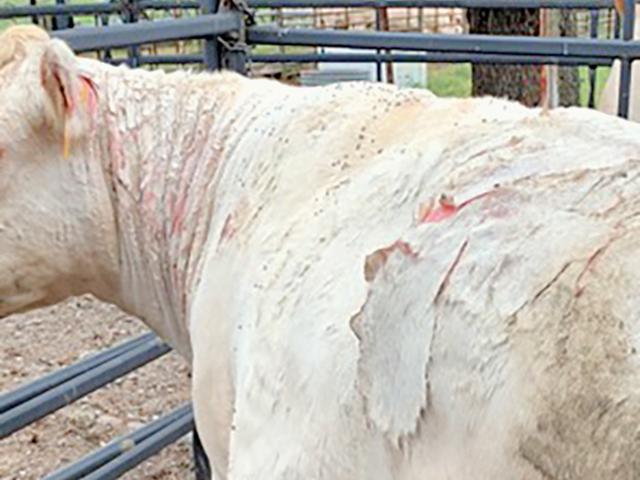
- Photosensitization:
- Dermatitis of light skin
- Absence of cyanosis of tongue
- Reddening and edema of skin

Treatment and Control:
- Broad spectrum antibiotics for secondary bacterial infection.
- Avoid grazing in areas where Culicoides available along with Culicoides control
- Polyvalent vaccine 2 ml SC route, Booster dose applied at 1 month
- Attempt should be made to control vector population by spraying insecticide and good water management.
- Contact with wild ruminants should be avoided.
- Quarantine of sick animals should be made.
- Import of animals from disease prevailing countries should be avoided.
- Strict regulation is to be followed to prevent entry of diseased animals from endemic zones.