Swine Dysentery:
- It is muco hemorrhagic diarrheal disease of pigs that affects large intestine.
- It is characterized by bloody to mucoid diarrhea and severe dehydration.
- It is most often observed in growing-finishing pigs and associated with reduced growth performance and variable mortality.
Etiology:
- Brachyspira hyodysenteria
- These spirochetes consistently produce strong β-hemolysis
- Gram-ve, helically coiled, oxygen tolerant, anerobic spirochete.
Transmission:
- Ingestion of infected feces
- Transmission can also occur through birds, flies, and fomites.
- Infected mice on premise may also be source of infection.
- Contaminated lagoon water and contaminated vehicles are important source of transmission.
Pathogenesis:
- Disease has got incubation period of 5-21 days
- Organism reaches to large intestine where it colonizes, proliferates and penetrates mucosal layer
- Bacteria produce toxins and hemolysin which cause tissue destruction and ultimately to mucohemorrhagic colitis.
Clinical Signs:
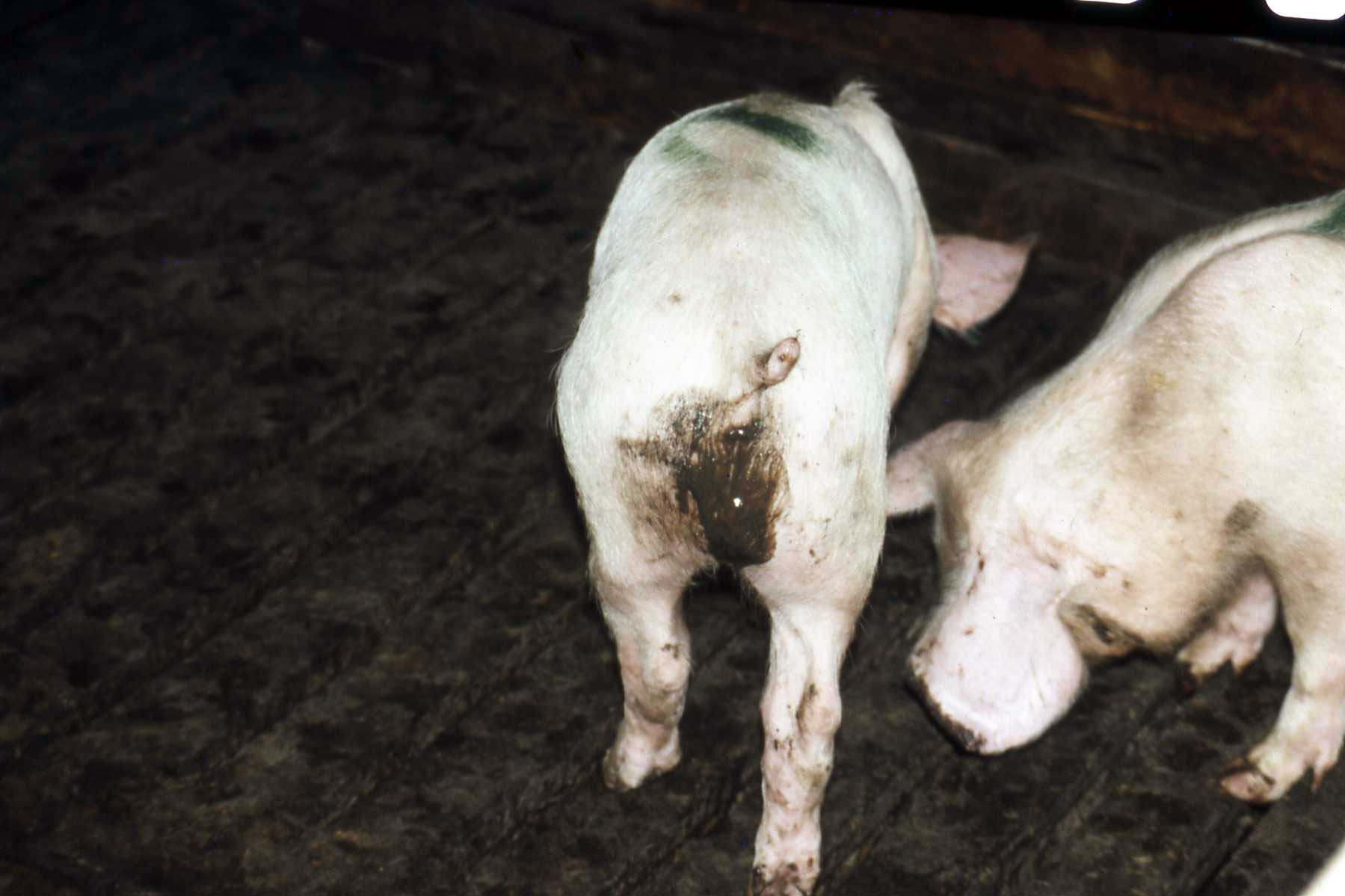
- Diarrhea; usually grey-yellow color, mucoid feces
- Diarrhea continues to become mucohemorrhagic with excess mucus and fresh blood apparent and moderate fever.
- Slightly depressed with reduced appetite.
- Skin discoloration in terminal stages
- Perineal area may be blood stained.
- Sunken eyes, marked weakness, hollow flanks
- Sudden death
PM Findings:
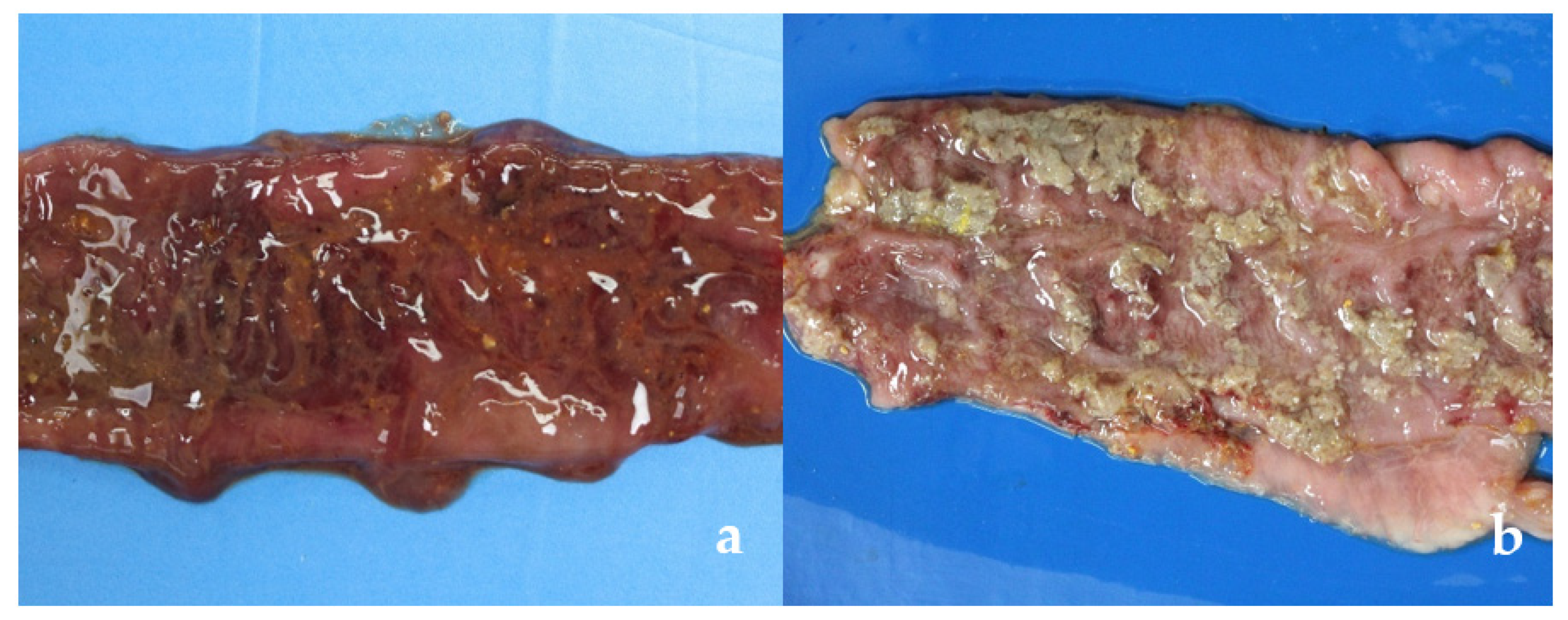
- Lesion are restricted to colon and cecum.
- Mesentery and serosa are edematous
- Large intestine is heavy, thick walled, congested and edematous
- Mucosa covered with fibrin, necrotic debris and mucus.
- Serosal hyperemia
Diagnosis:
- Based on clinical findings
- Based on PM findings
- Demonstration of spirochetes in stained smear made from colonic scrapping
- Serological test: ELISA
Treatment:
- Tiamulin @10-15 mg/kg, b.wt. IM x SD
- Carbadox @ 50mg/kg, of feed for 30 days
- Carbadox combined with sulfamethazine @100 mg/kg, of feed for 30 days
- Lincomycin @ 11mg/kg, b.wt. IM, OD, for 5-7 days
Control Measures:
- Strict quarantine measures should be followed.
- Biosecurity measures such as restriction of movement of vehicles, animals, humans onto farms.
- Disinfection of farm premises with suitable disinfectant; sodium hypochlorite, iodophores.
- Mass medication and sanitation program should be followed.