Asexual Propagation in Plants
- Asexual propagation or vegetative propagation refers to the multiplication or perpetuation of any plant from any vegetative parts as plant other then the seed
- It is independent of sexual propagation process
- It takes place due to mitosis division ( when some portion of plant is wounded, mitosis division take place)
- The plants raised through asexual process are identical to mother plants
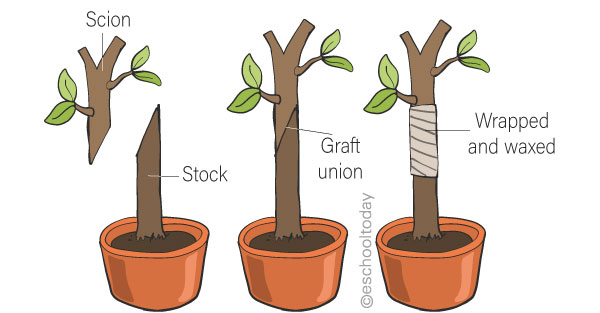
- Cutting, budding, and grafting, and layering are main methods of asexual propagation
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation:
- The progenies are true to type like mother plant
- Vegetative propagation is the only alternate where no seed is formed or germination of seed is very slow or no viable seed is formed. (e.g. Banana, Pine apple and roses, seedless grape)
- Certain rootstock has the capacity of resisting or tolerating the adverse environment factors such as frost and adverse soil factors like salinity or alkalinity E.g. frost resistance, Poncirus trifoliate (Trifoliate orange)
- The ability of certain rootstock to resistant pest and diseases can be advantageously expected An apple when grafted on rootstock like Merton series is resistant for wooly aphid
- Vegetative propagated plants are generally dwarfed in nature than the seedlings. Dwarf trees facilitate pruning spraying and harvesting easy seedling. Dwarf trees facilitate pruning, spraying and harvesting easy and more number of plants can be accommodated in a unit area
- To replant an undesirable existing tree either with reference to its quality or susceptibility to pests and diseases. The defect can be overcome easily by vegetative propagation through grafting or budding of desirable scion to the existence tree by top working technique
- Many plants are propagated by vegetative means because of the speedy easy of multiplication
- Novelty can be developed by grafting or budding on single plant many varieties. E.g. Roses
- To convert inferior varieties in superior. Example side grafting in mango
Disadvantages:
- Plant is not vigorous and long lived
- No new varieties are evolved or developed
- These methods are expensive and laborious and time consuming