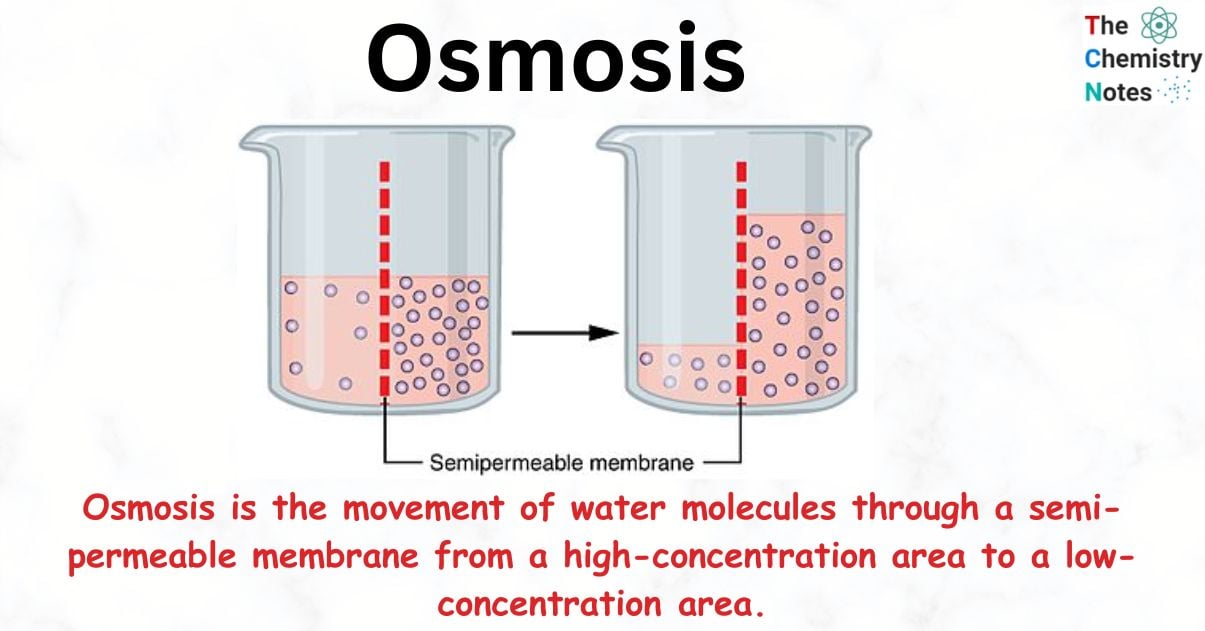
Osmosis:
The movement of water or solvent from a region of its higher concentration to lower concentration through semi permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Types of osmosis:
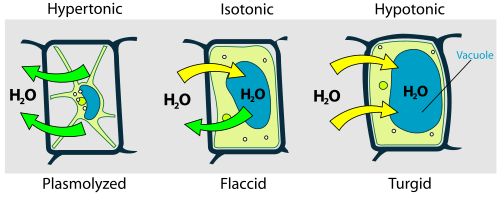
- Exosmosis : The outward movement of water from a cell when placed in a hyper tonic solution is called exomosis. In this case, water diffuse from the cell because of exosmosis and cell is flacid.
- Endosmosis: When a cell placed in a solution of lower concentration of solute(hypo tonic), the water enters inside the cell. This is called endosmosis. By endosmosis, cell is turgid.
Types of solution:
- Hypertonic: In this solution, the amount of solute is higher than the solvent.
- Hypotonic : In this solution, the amount of solute is lower than the solvent.
- Isotonic : in this solution, the concentration of solute and solvent are same.
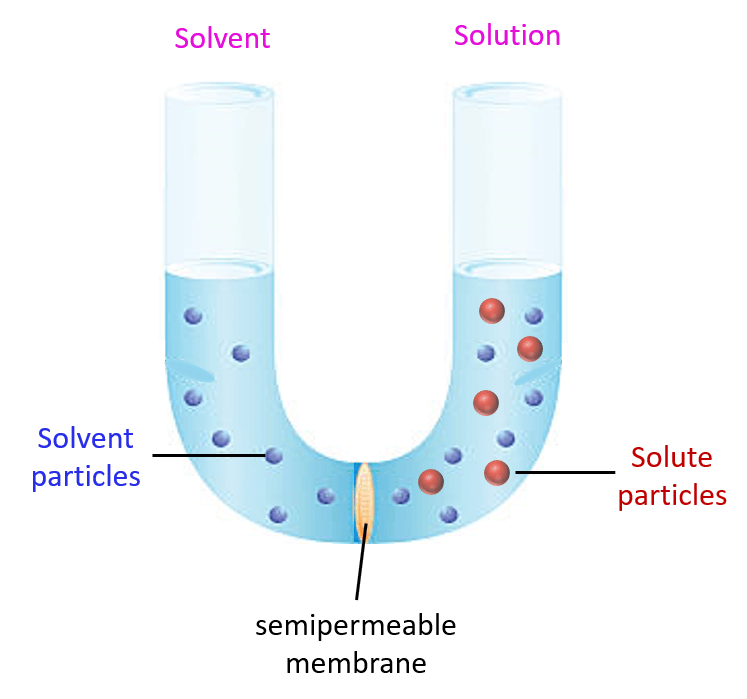
Permeability of a membrane:
- Permeable membrane : The membrane which allows free movement of water and solute into and out of the cell is called permeable membrane. Eg: Filter paper.
- Impermeable membrane: The membrane which don’t allow the passage of both water an solvent into and out of the cell is called impermeable membrane. Eg: Rubber membrane.
3.Semi-permeable membrane: The membrane which allow passage of only limited molecules of solvent selectively is called semi-permeable membrane. Eg: Plasma membrane.
Osmotic pressure:
Osmotic pressure is defined as the pressure required to prevent the net movement of pure water into a solution.
Turgor pressure:
It is the pressure developed inside a cell which press the protoplasm against the cell wall and cell become turgid.
Wall pressure:
The pressure exerted by the cell wall against protoplasm due to osmosis is called wall pressure.
When Tp = Wp; cell is turgid.
