Dark reaction or Calvin cycle or C3.
In the second phase of photosynthesis which is independent of light. The ATP and NADPH are produced by the light reaction utilized in the dark reaction to reduce carbon dioxide to carbohydrate by a process called carbon fixation. It occurs in stoma of chloroplast. Dark reaction was discovered by calvin in 1954. Therefore, it is called calvin cycle or C3 cycle. Dark reaction can be studied under three headlines.
1.Carboxylation:
In this step, atmospheric CO2 accepted by RUBP (Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate) in the presence of enzyme Rubisco. The three molecules of RUBP react with 3 molecules of CO2 to form 3 molecules of 6 carbon unstable compound which is converted into PGA. PGA ( 3 carbon compound) is the first stable product. So, it is called C3 cycle.
RUBP + CO2 ————–> 6 carbon stable compound.
6 carbon unstable compund + H2O ———> PGA (Phosphoglyceric acid)
- Glycolytic reversal :
This process involves conversion of three PGA to glucose molecules in many steps. This Process is the reverse of the oxidation step in glycolysis. So, called glycolytic reversal. It involves following steps:
a) 3 PGA + ATP 1,3- diphosphoglyceric acid + ADP
b) 1,3- diphosphoglyceric acid
c) 3- Phosphoglyceraldehyde dihydroxy acetone-3-phosphate (DHAP).
d) DHAP + PGAL Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
e) Fructose-1,6-diphosphate + H2O Fructose-6-Phosphate + H3PO4
f) Fructose-6-phosphate Glucose-6-phosphate
g) Glucose-6-phosphate Glucose + starch
- Regeneration of RUBP
Fructose-6-phosphate and 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate react to form erythose-6-phosphate and xyulose-5-phosphate. The erythose phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate combine to form sedoheptolase-7-phosphate which regenerate RUBP in many reactions.
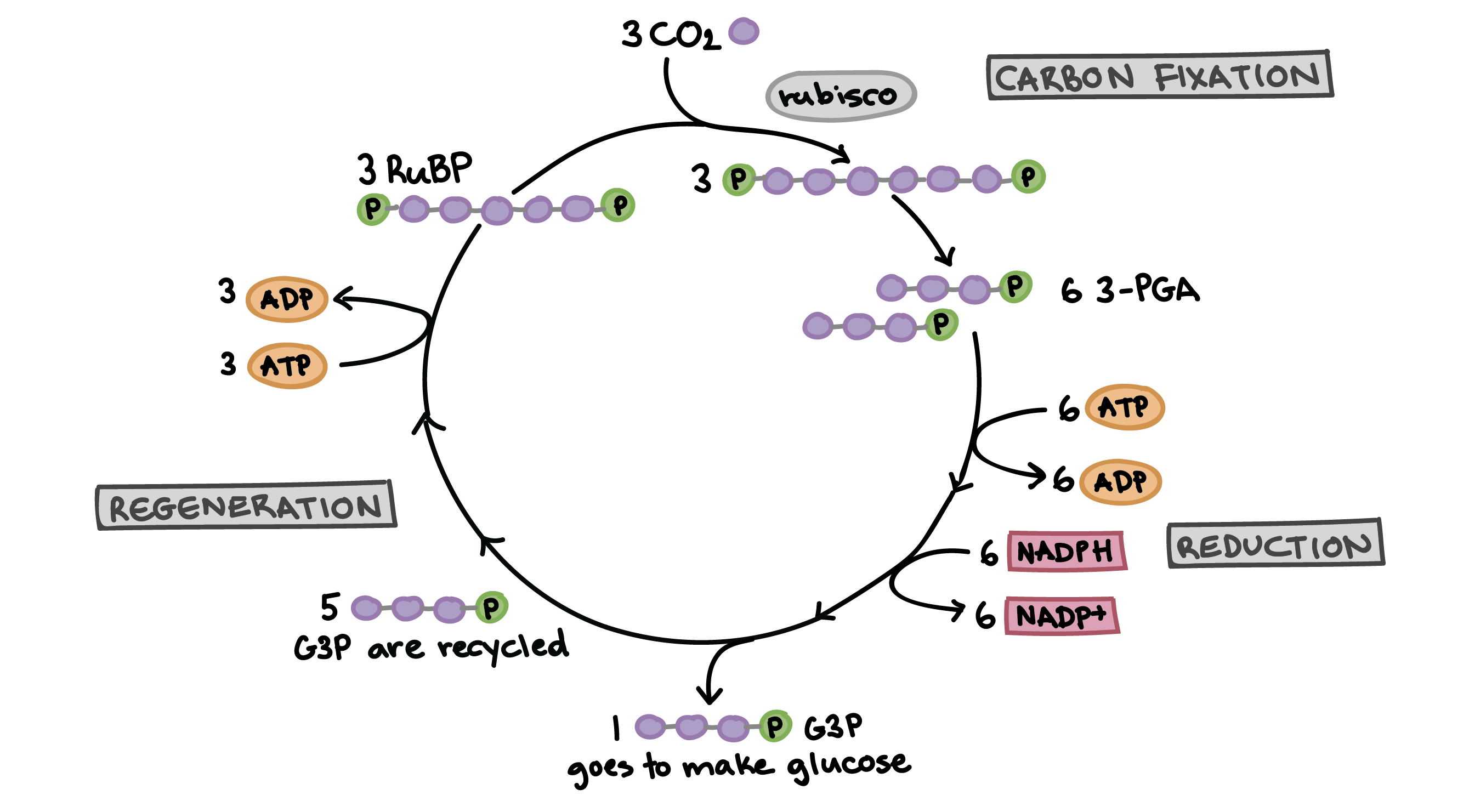
Fig: C3 cycle or calvin cycle or dark reaction