Mechanism of Respiration
The process of respiration completes in 4 major phases:
- Glycolysis :
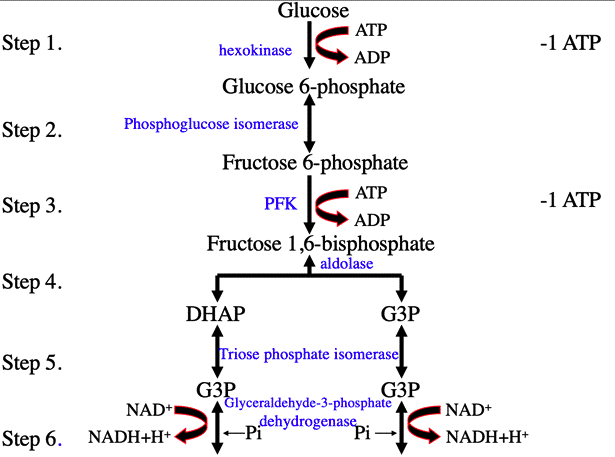
It is common to aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occur in cytoplasm. In this process , oxygen is not necessary and a glucose molecule breaks to form two molecules of pyrubic acid under the action of several enzymes.
- Oxidative decarboxylation of pyrubic acid:
Pyrubic acid is the end product of glycolysis that don’t enter into kreb cycle directly so three carbon carbon change into 2 carbon atom, acetic acid by decarboxylation. Acetic acid enters into mitochondrial unit and react with Co-enzyme A to form acetyl Co-enzyme A. In this reaction, two hydrogen atom are released , accepted by NAD to form NADH2.
In glycolysis, two molecules of pyrubic acid, two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of ATP are formed.
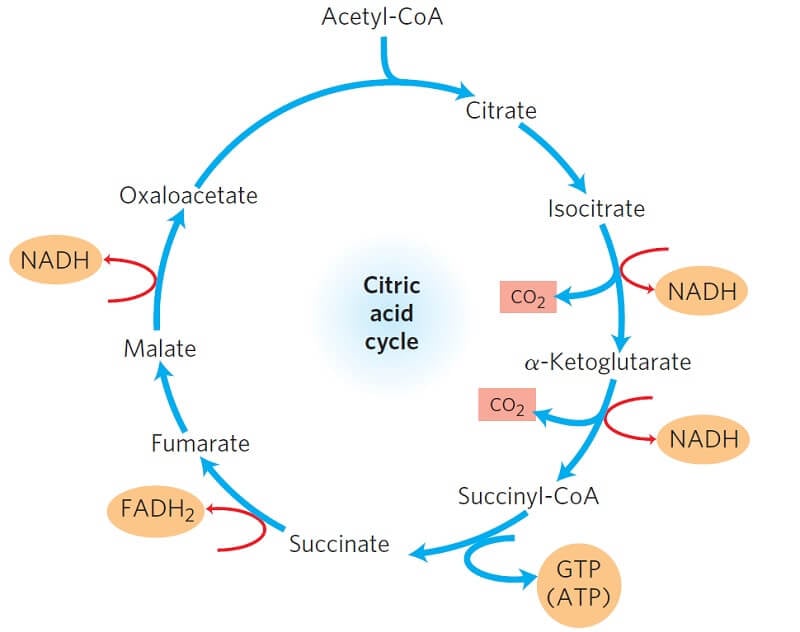
- Kreb’s Cycle :
Acetyl C-enzyme A enters into matrix of mitochondria and decarboxylated dehydrogenated into CO2, water, NADH2 and FADH2 in presence of oxygen to release ATP energy in kreb cycle. The first metabolic compund of Kreb’s cycle is 3-carbon atom, cytric acid. So, it is also called tricarboxylic acid cycle. It was discovered by Kreb in 1945 and got Noble Prize in 1950.