Electron Transport System (ETC)
During respiration simple carbohydrates and intermediate compounds like phosphoglyceraldehyde, pyruvic acid, isocitric acid, ά ketoglutaric acid, succinic acid and malic acid are oxidized. Each oxidative step involves release of a pair of hydrogen atoms which dissociates into two protons and two electrons.
2H 2H+ + 2eThese protons and electrons are accepted by various hydrogen acceptors like NAD,NADP, FAD etc. After accepting hydrogen atoms these acceptors get reduced to produce NADH2, NADPH2 and FADH2. The pairs of hydrogen atoms released a series of coenzymes and cytochromes which form electron transport system, before reacting with O2 to form H2O.
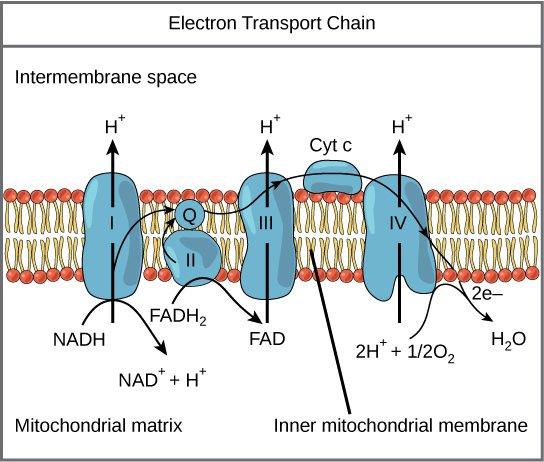
The composition of each of the respiratory chain complexes is shown below
|
Components of electron transport system:
- The electron transport system is made up of following enzymes and proteins:
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
- Flavoproteins (FAD and FMN).
- Fe-S protein complex.
- Co-enzyme Q or ubiquinone.
- Cytochome-b
- Cytochrome-c1.
- Cytochrome-c
- Cytochrome-a
- Cytochrome-a3.
All the above enzymes are found in F1 particles of mitochondria.