Classification of polysaccharide
A. Homopolysaccharide:
- Contain single type of monomeric units.
- Some serve as starch in plant and glycogen in Animal.

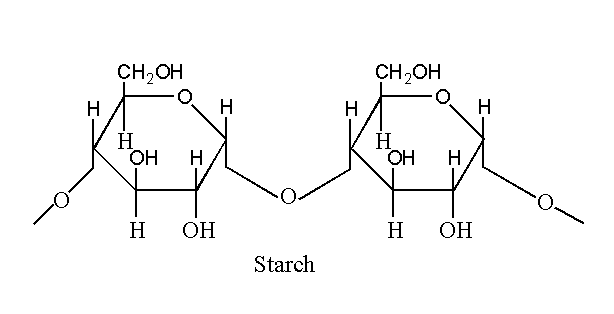
I. Starch:
- Abundant in tubers of potatoes and seeds.
- Starch contains two types of glucose polymer. i.e., Amylase ( long unbranched chain of D-glucose units) and Amylopectin (Highly branched).
II. Cellulose:
- Fibrous, tough, water insoluble substance in the cell wall of plants particularly in trunk, stem, etc.
- Everything is same between D-glucose and Arabinose except -CH2OH group is replaced by -H bond.
- This bacterial metabolism is often associated with the production of uncomfortable volume of gas, chiefly CH4 and H2.

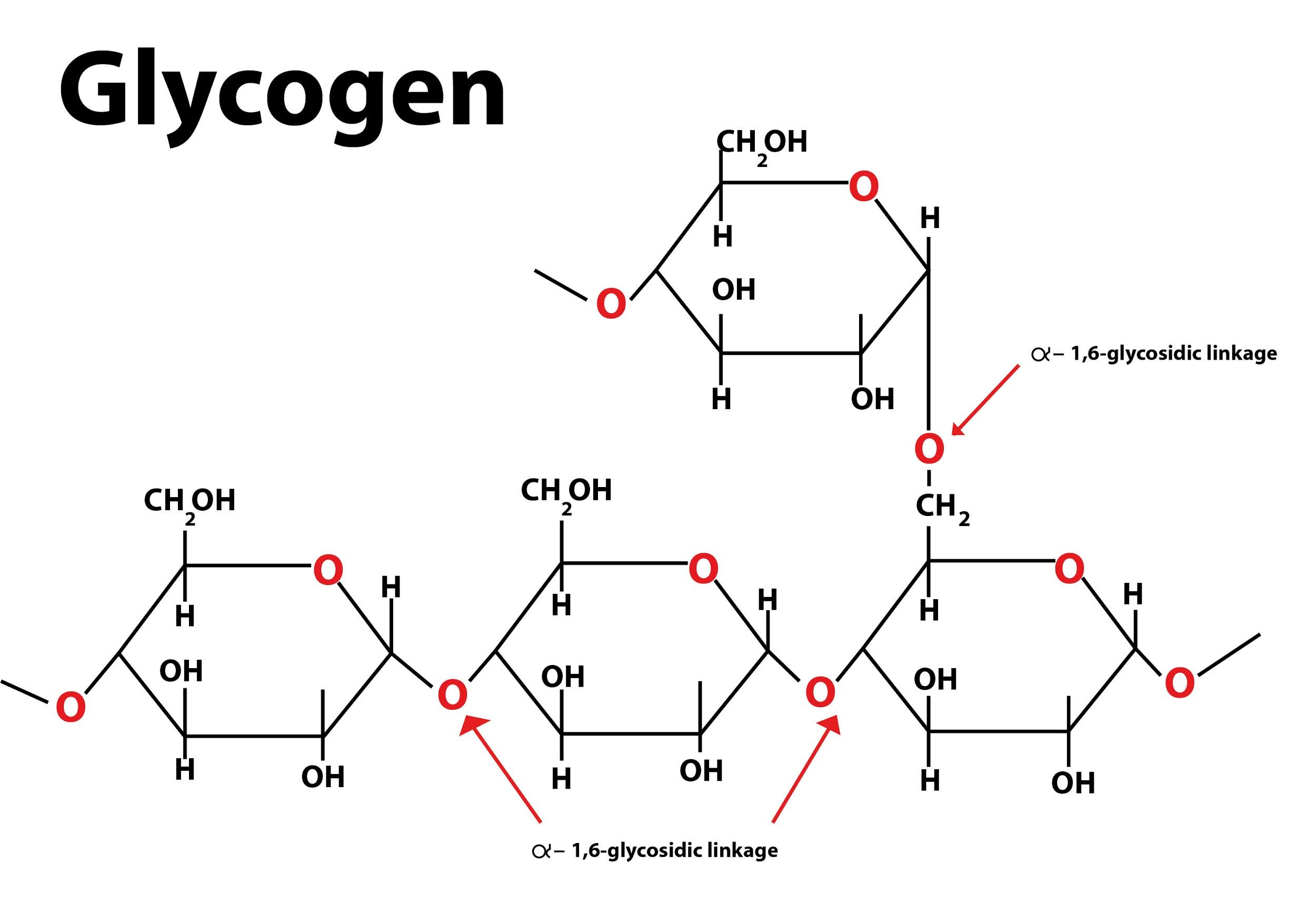
III. Glycogen:
- Main Storage polysaccharide of animal cells.
- Glycogen is specially abundant in liver and constitute about 7% of the wet weight.
- Average chain length is only 8 glucose units.
- Molecular mass is very high and gives red color with iodine.
- Open circle represents glucose units.
- Chin length is 8 glucose units in Average.
IV. Chitin:
- Linear homopolysaccharide composed of N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine residues in β-linkage.
- The only difference from cellulose is the replacement of hydroxyl group of C-2 with an acetylated group.
- Indigestible by vertebrate animals.
- Chain of 3-Muramic acid.
B. Heteropolysaccharide:
- Contain two or more different kinds of monomeric units.
- Provide extracellular support to organism.
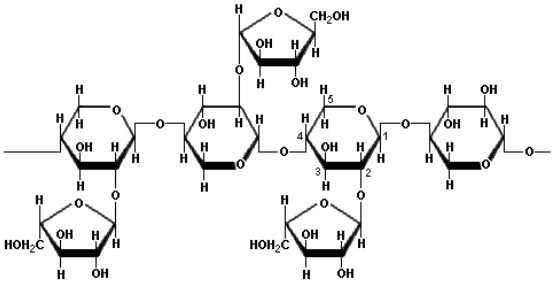
I. Glycosaminoglycans:
- Are linear polymers of repeated disaccharides and in most cases hexosamine.
- Are strongly acidic. Eg: Hyalauronic acid.
a. Hyalauronic acid
- Is linear polymer of glucuronic acid and N-Acetylglucosamine.
- There is no sulphate ester.
