Introduction
- Microorganisms are microscopic, unicellular to multicellular living organism and are ubiquitous in distribution i.e. they are found in soil, water, air, death and decayed matters of plants and animals.
- Usually parasitic microbes behave as pathogenic and produce many diseases in plants and animals.
- Here we study only plant pathogenic microbes, which develop disease in the plants.
- The plant pathogenic microbes can be classified under algae, fungi, bacteria, virus and nematodes.
Algae:
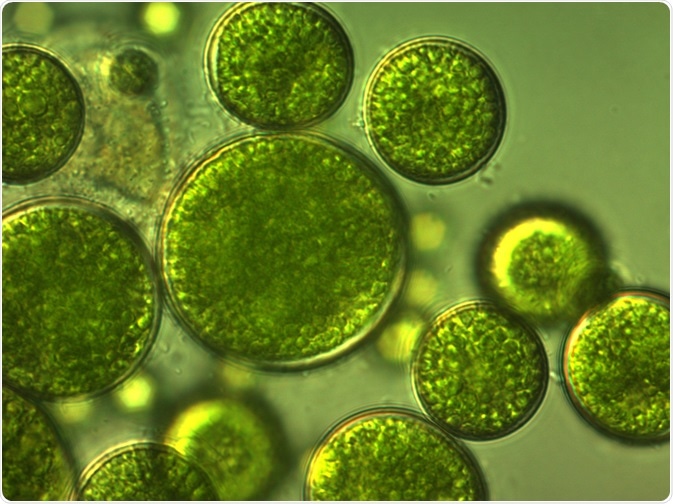
- Algae possess chlorophyll and are able to manufacture their own food.
- Being self-sufficient in this aspect, they are seldom found to depend on other plants in pathogenic condition.
- One exceptional case is that Rust disease is caused by species of Cephaleuros.
E.g.: Cephaleuros virescens and Cephaleuros parasities are two common species found on the citrus, mango, cashewnut, guava and other fruit tree and on tea and coffee plants.
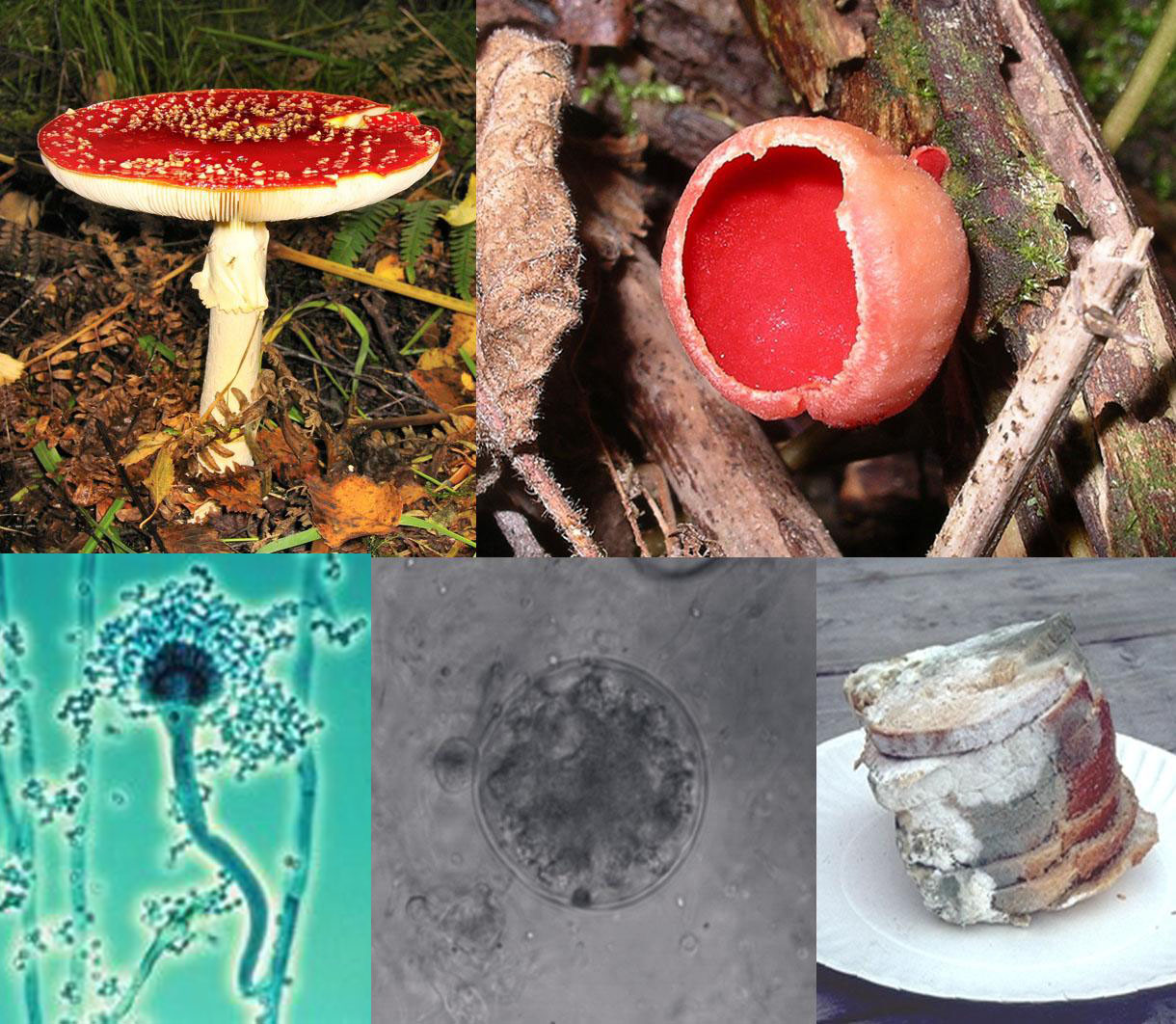
Fungi:
- Eukaryotic , heterotrophic, achlorophyllous, spore bearing organisms whose nucleated somatic bodies are usually surrounded by cells well containing cellulose or chitin or both and reproduce asexually or sexually.
- Some of the fungi behave pathogenic and cause diseases which are listed below:

|
S.N. |
Fungal Pathogens: |
Diseases |
|
1. |
Phytophthora infestans |
Late blight of potato |
|
2. |
Phytophthora plamivora |
Bud rot of palm |
|
3. |
Pythium debaryanum |
Damping off seeding |
|
4. |
Pythium graminicola |
Root rot of wheat |
|
5. |
Physoderma zeamaydis |
Brown spot of maize |
|
6. |
Erysiphe polygonii |
Causes powdery mildew of pea |
|
7. |
Claviceps purpurea |
Ergot disease of Bajra |
|
8. |
Albugo candida |
White rust of crucifers |
|
9. |
Puccinia graministriticii |
Black rust of wheat |
|
10. |
Taphrina deformans |
Leaf curl disease of peach |
Mycoplasma:
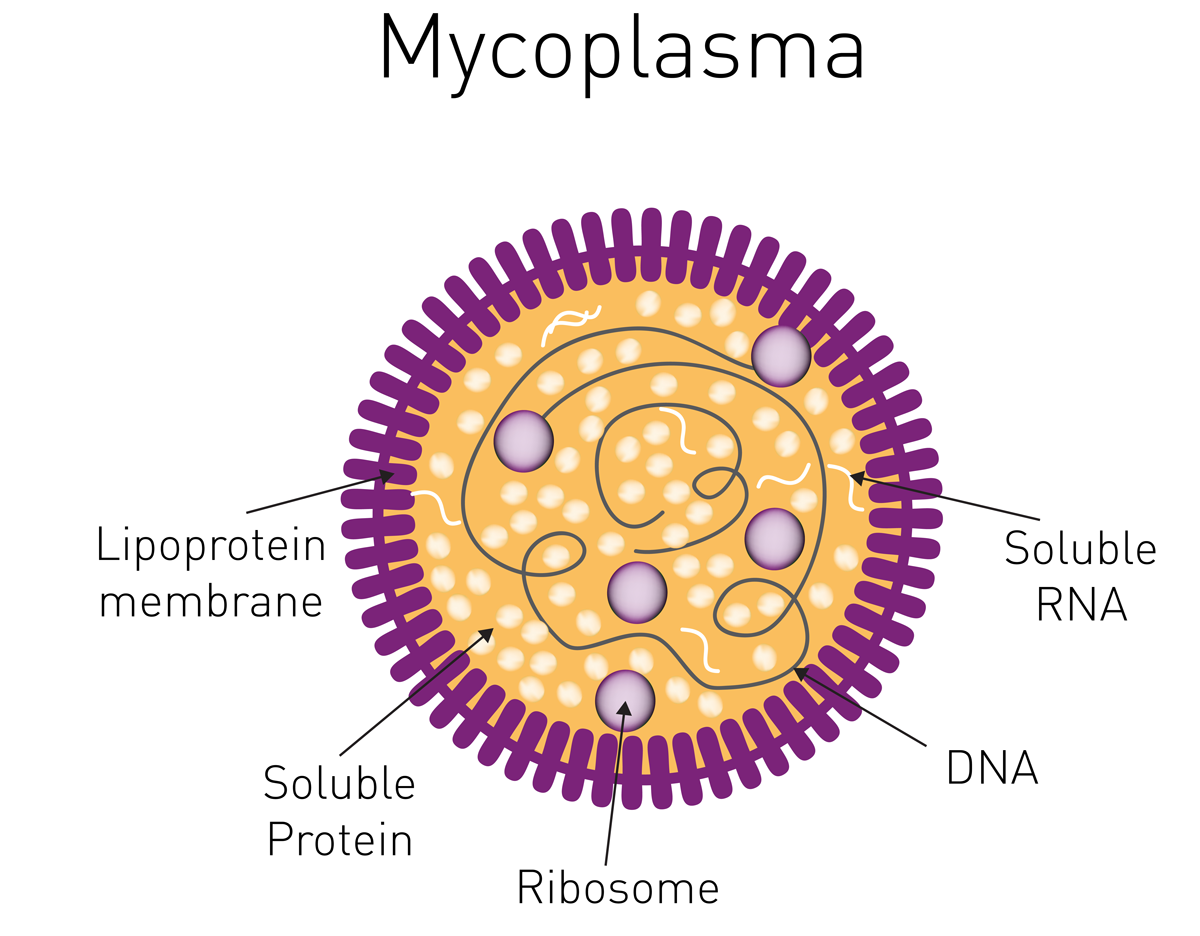
- These are commonly called as pleuropneumonia like organisms (PPLO’S).
- It is smallest cell wall-less, free living, self-replicating unicellular prokaryotic organisms.
- Cell is limited by trilaminar plasma membrane.
- Cytoplasm contains ribosomes, double stranded DNA.
- The cells have plasticity and can modify their shape in many shapes ranging from spherical to branched filaments.
Mycoplasma disease:
a). Sandle wood spike
b). little leaf disease of brinjal
c). Clover phylloidy
d). Grassy shoot disease of sugarcane
e). Witch broom disease of Potato
f). Tomato big bud
g). Aster yellow’s
Nematodes:
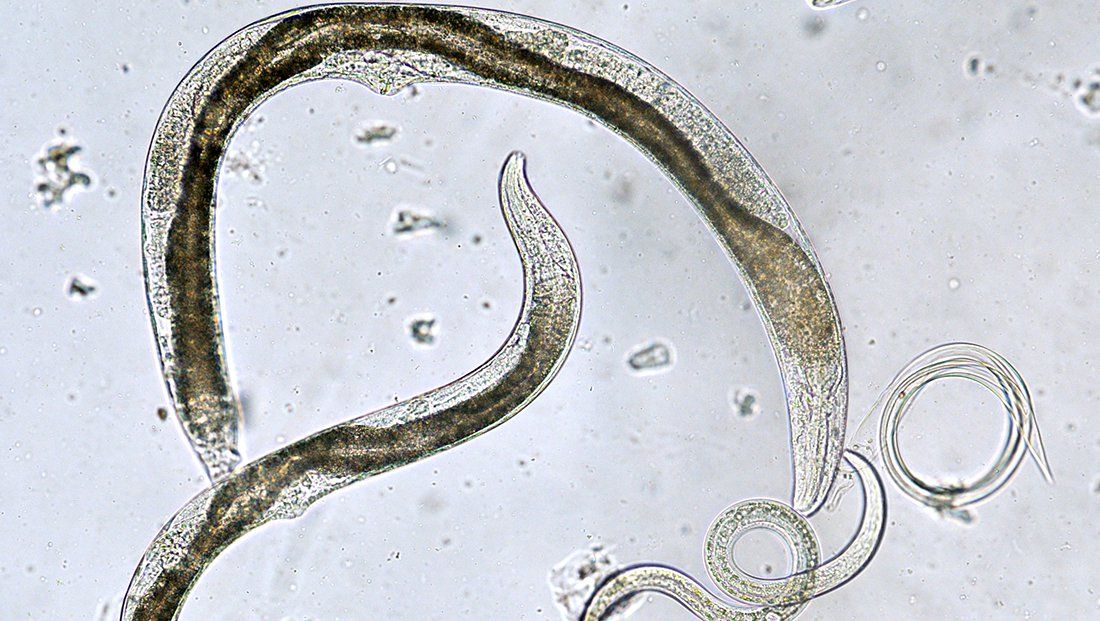
- They are plant parasitic organisms having 300-1000 µ in length and 15-35 µ in breath.
- Eeel shaped, round in cross section with smooth unsegmented bodies without legs.
- The body is covered with smooth cuticle.
Root knot of vegetables (Cucurbits, potato, tomato, brinjal, chillies)
- Lady’s finger, groundnut, carrot, radish or arum (Colocasia esculentum)
Causal Organisms: Meloidogynae spp., Meloidogynae javanica, Meloidogynae arenaria etc.
- Molya disease of barley and wheat- Heterodera avenae
- Ear cockle of wheat – Anguina tritici
- Ufra disease of rice – Dytilenchus langustus
- Nematode disease of rice – Rhodophalus oryzae