Bacteria
- These are true prokaryotic organisms.
- There are different types of bacteria which are known as True bacteria (Eubacteria) & Nucleated organism (Archaebacteria, Cyanobacteria, Mycoplasmas etc.)
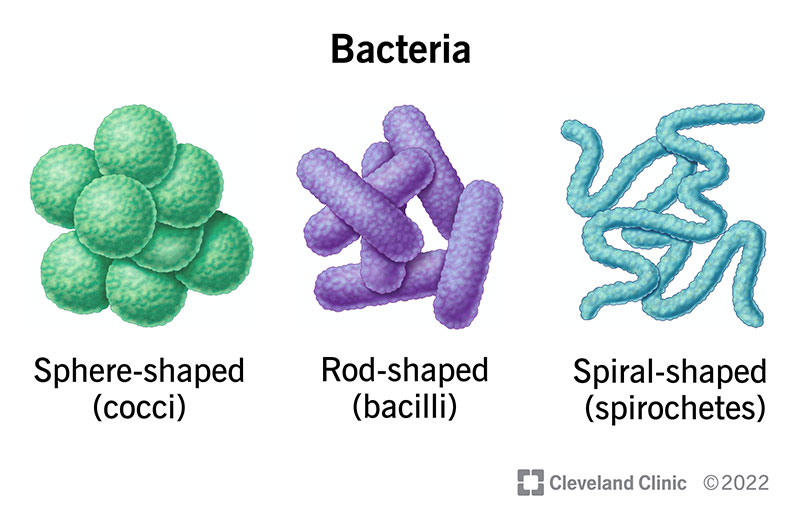
Types of bacteria
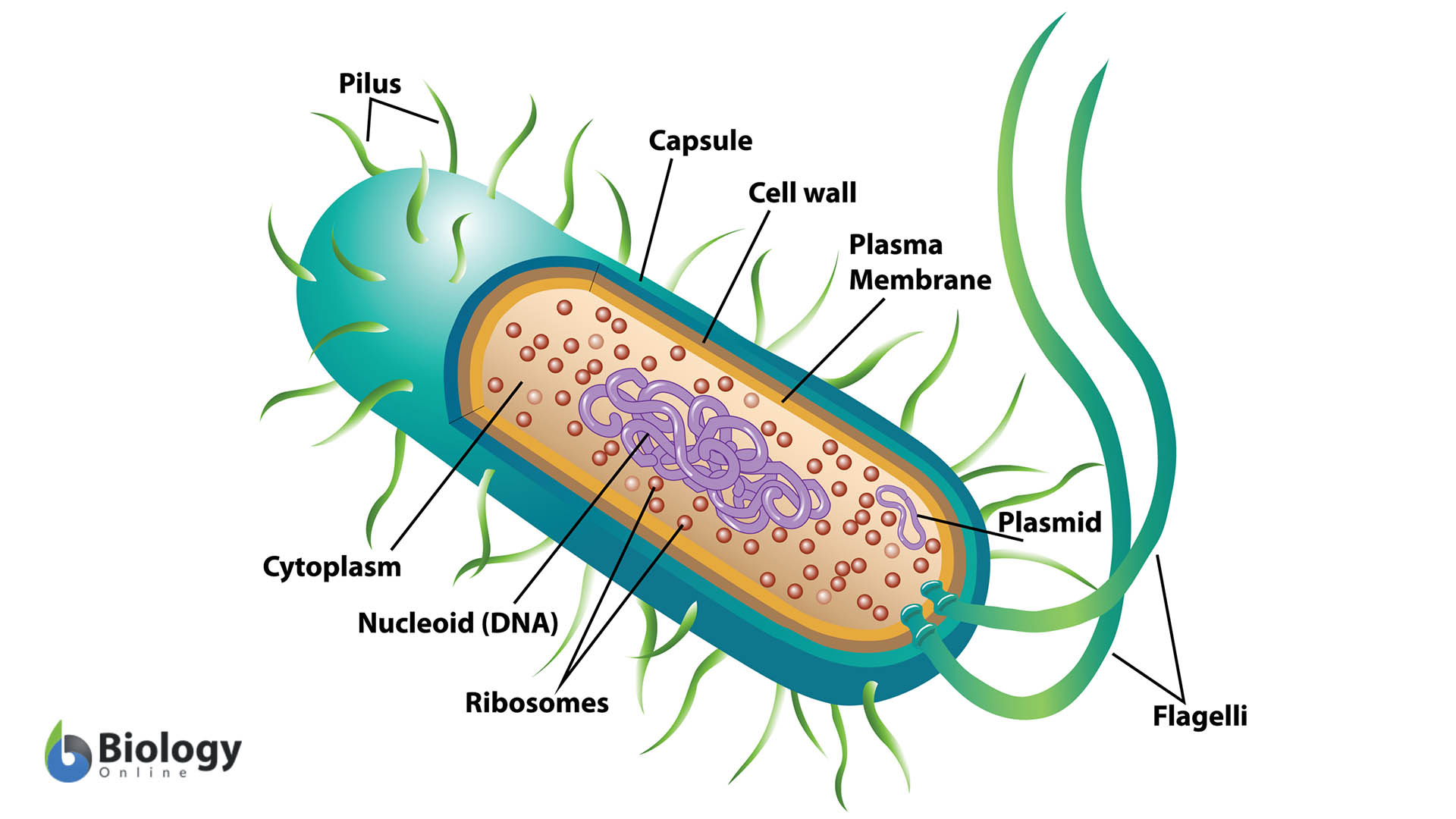
1.Eubacteria:
- They have either of following shapes.
a)Coccus: Micrococcus, Halococcus
b)Bacillus: Lactobacillus, Thiobacillus
c)Comma
d)Spirillum
e)Vibrio
- They reproduce by binary fission.
- Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan.
- On the basis of gram strain; Gram +ve: Peptidoglycan thick and Gram –ve: peptidoglycan thin.
- Can occur in both oxygen abundant & oxygen deficient regions
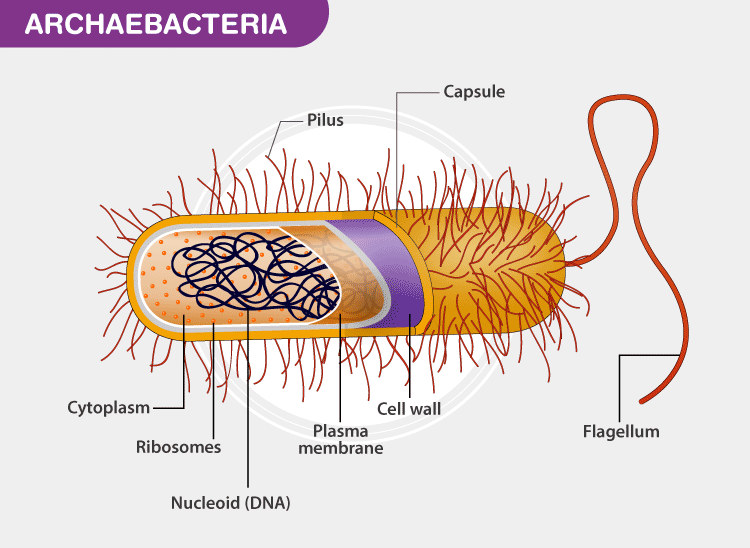
- Archaebacteria:
- Cell wall do not contain peptidoglycan but contain other polysaccharides.
- Cell membrane contains a single layer of glycerol hydrocarbons glycerol chains instead of bicay of phospholipid arranged tail to tail.
- Their ribosomes are insensitive to chloramphenicol (Antibiotics).
- Include methanogens (methane generating bacteria): Halophiles (salt loving) & Thermoacidophile (high temp. & acidic pH, sulfur spring, cools waste).
3. Cyanobacteria:
- Typical prokaryotes
- Evolve O2 during photosynthesis.
- Found in terrestrial and aquatic environment e.g.: Nostoc, Anabaena, Oscillatoria etc.

- Actinomycetes:
- Majority of Actinomycetes are mycelial (as in fungi) and gram +ve.
- Reproduce by unicellular specialized spores.
- g.: Streptomycetes, Micromonospora etc.
- While in other the mycelia state is transitory and of ten limited producing no specialized spores & reproducing by fragmentation forming short rod-shaped cells.
- Eg.: Actinomycetes, Nocardia and Mycobacterium: medicinally important.
