Genetics of bacteria
- The change in genome is usually brought about by mutation and by transfer of genes between organisms.
- Bacteria are generally haploid and genes transferred in bacterial cells don’t form zygote but partially diploid are produced called merozygotes.
- The original genome of the recipient is named as endogenote and a portion of DNA introduced from a donor cell in to the recipient cell is called exogenote.
- Variation in sequence or grouping of genetic nucleotides is called recombination and this mechanism is known as recombination mechanisms.
Mechanism of Recombination
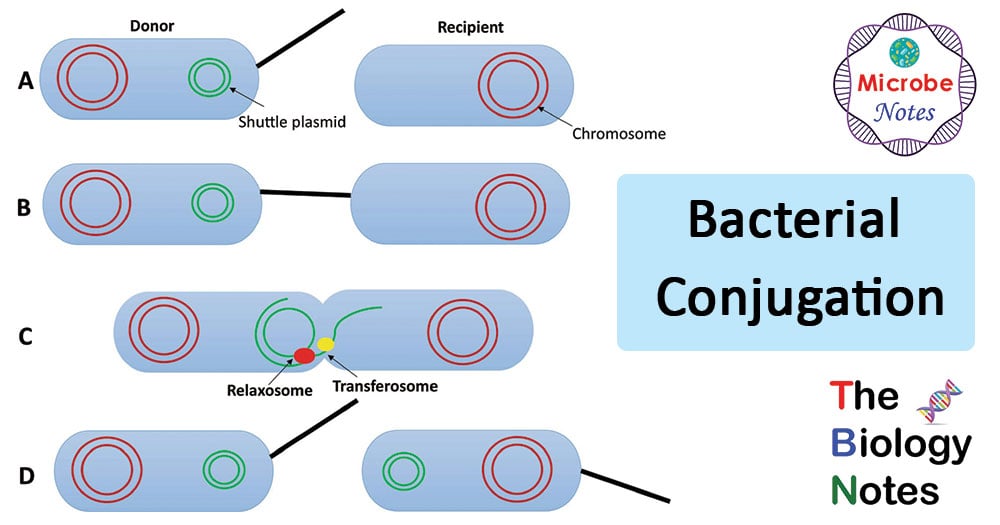
- Conjugation:
- Most common process of reproduction and includes the direct transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another.
- In conjugation, two bacteria lie close together and a connection forms between them.
- A plasmid or a part of the bacterial chromosome passes from one cell (the donor) to the other (the recipient).
- Subsequent to conjugation, crossing over takes place between homologous sequences in the transferred DNA and the chromosome of the recipient cell.
- In conjugation, DNA is transferred only from donor to recipient, with no reciprocal exchange of genetic material.
- Transformation:
- DNA in the medium surrounding a bacterium is taken up.
- After transformation; recombination may take place between the introduced genes and those of the bacterial chromosome.
- Griffith (1928) initially conducted the experiment on transformation.
- In transformation, the genetic material is transformed from one shape to another form.
- In several bacteria like Bacillus, Salmonella, Streptococcus, Rhizobium etc., normally transformation of genes (incipient DNA and RNA) occurs but in E. coli doesn’t occur.
- The main function in this type is; DNA from donor cell is incorporated in the chromosomes of receptor cell and transformed thereby in a cell with entirely new properties.

- Transduction:
- bacterial viruses (bacteriophages) carry DNA from one bacterium to another.
- Once inside the bacterium, the newly introduced DNA may undergo recombination with the bacterial chromosome.
