Types of factor-factor relationship
1.Fixed proportion combination:
- This relationship holds if inputs are added in fixed proportion at all levels of production.
- A driver and a tractor combination is an example of it.
- The inputs which increase the output only when combined in a fixed proportion are known as complements.
- Substitution of one input or group of inputs with other input or group of inputs can take place at different rates.

- Constant rate of substitution:
- The substitution at constant rate occurs when the amount of one input replaced by the other input does not change as the added input increases in magnitude.
- The rate at which these two inputs can be substituted at a given level of output is constant regardless of the level of the two inputs used.
- It is commonly called the marginal rate of substitution between the inputs and is denoted by ΔX2/ΔX1 which is the slope of the product.
Table: Constant rate of substitution for producing 100 units of output
|
X2 (Women labor) |
X1(Men labor) |
ΔX2 |
ΔX1 |
ΔX2/ΔX1 = (MRS) |
|
10 |
1 |
– |
– |
– |
|
8 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2/1= 2 |
|
6 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
4 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
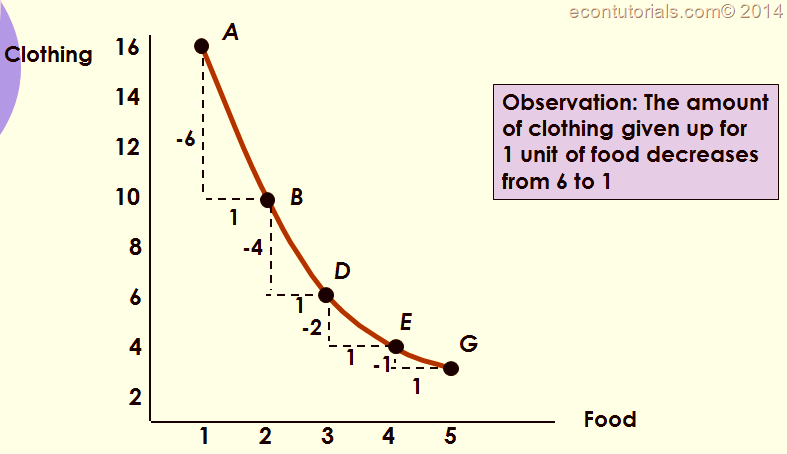
- Varying rate of substitution:
- The amount of one input (X1) required to substitute for one unit of another input (X2) at a given level of production increases or decreases as the amount of X1 use decreases.
- The slope of iso-product curve in this case becomes less steep as more of X1 is used relative to X2.
- Thus, decreasing rate of substitution means that every subsequent increase in the use of one factor replaces less and less of the other.
- Examples are substitution among concentrates and green fodder, labor and capital, and nitrogen and phosphorus.
Table: Decreasing rate of substitution for producing 100 units of output
|
X2 |
X1 |
ΔX2 |
ΔX1 |
ΔX2/ΔX1 =(MRS) |
|
23 |
0 |
– |
– |
– |
|
16 |
1 |
7 |
1 |
7 |
|
10 |
2 |
6 |
1 |
6 |
|
5 |
3 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
1 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
0 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
