Discounted measure:
– It considers time value of money.
– The major concept of this is that money available at the present time is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity.
– This core principle of finance holds that, provided money can earn interest, any amount of money is worth more the sooner it is received.
It includes:
A) B/C ratio:
– It is defined as the ratio of discounted benefit stream to discounted cost stream.
– OR it is the ratio of present worth of incremental benefit stream (cash inflows) to present worth of incremental cost stream (cash outflows) due to enterprise.
– When it is expressed in percentage it is called profitability coefficient.
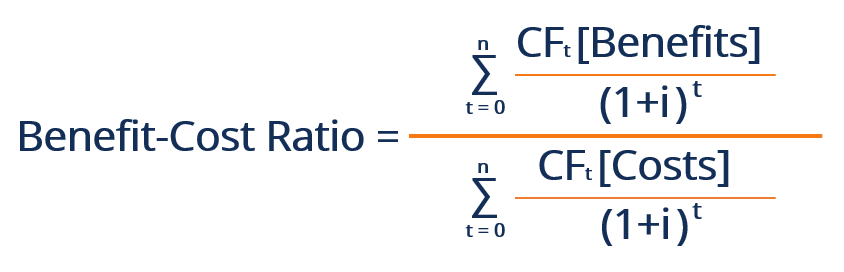
Note : The absolute value of BCR will vary depending on the interest rate chosen. The higher the interest rate, the smaller the resultant benefit-cost ratio.
Decision Criteria:
I) If the B/C ratio is greater than 1 project is accepted.
ii) If the B/C ratio is less than1 project is rejected.
iii) If the B/C ratio is one than decision is indifference.
Benefits
– NPV and B/C ratio are similar because if NPV is +ve then B/C ratio is greater than 1.
– This method is simple and easy to calculate.
– Used in ranking the mutually exclusive project but cannot be used in ranking non-mutually exclusive projects.
Demerit
– This method discriminate with the projects with low B/C ratio but have large wealth generating capacity than the alternatives with higher B/C ratio but low income generating capacity.
B) Net present worth:
– The present worth of the benefits less the present worth of the costs of a project called NPV/NPW.
– It is present value of incremental net benefit.
– It is the discounted profit in absolute form.
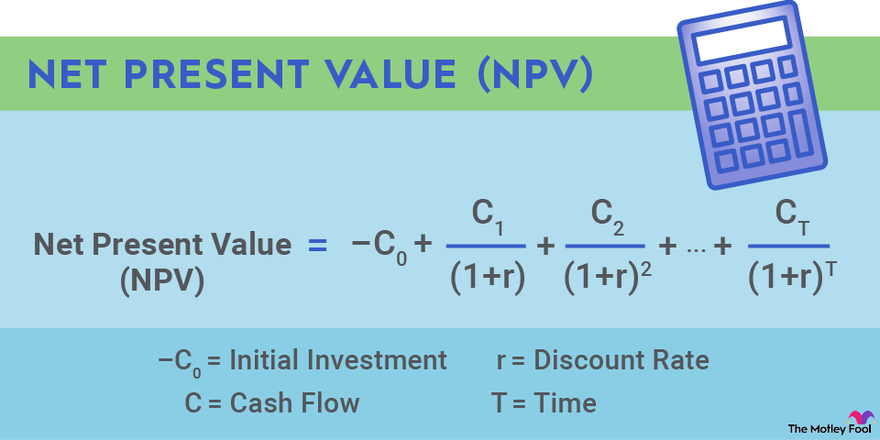
Decision criteria:
a) NPV +ve = Accepted
b) NPV -Ve = Rejected
c) NPV 0 = Indifferent
Merit
– It is good for those seeking the higher profitability
– Good for selecting the mutually exclusive project e.g. bigger dam vs smaller dam. Furrows sprinkler irrigation.
Relationship between Discount rate and NPV
– Inverse relationship
Limitation
– NPV is not useful for comparison if initial investment amount are different.
– Let two initial investment 70 lakh and 20 lakh have both NPV 1 crores
In this case the higher investment is selected because it creates multiplier effects in economy by creating wings of employment and social welfare .e.g. in investing poultry enterprises, driver, labor, vet doctors, accountant etc. will get employment opportunities.
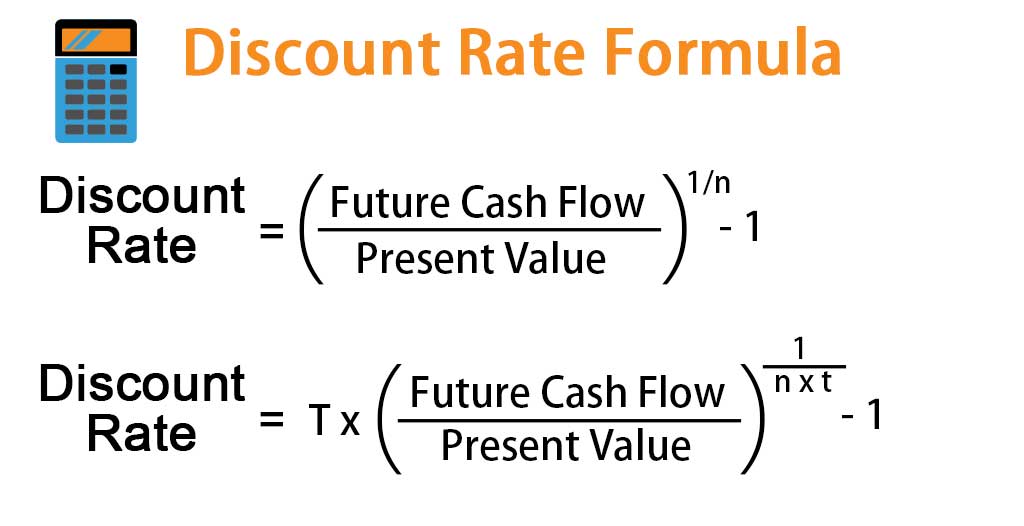
c) Discount rate
– It is rate at which an agent determines present worth of future cash flow.
– Generally interest rate is used as discount rate
d) Required rate of return
– It is rate of return below which investor does not wants to invest.
– It is also called as opportunity cost of capital.
– By using required rate of return investor discount his cash flow and find the worthiness of business.

Mathematically,
Required rate of return = I + risk premium + service charge + etc.
e) Internal rate of return (IRR)
– The internal rate of return of a project is the discount rate, which makes its net present value equal to zero i.e. present value of benefits equals’ present value of cost.
– It is the maximum interest rate that the project can pay.
– It is the maximum earning capacity of project.
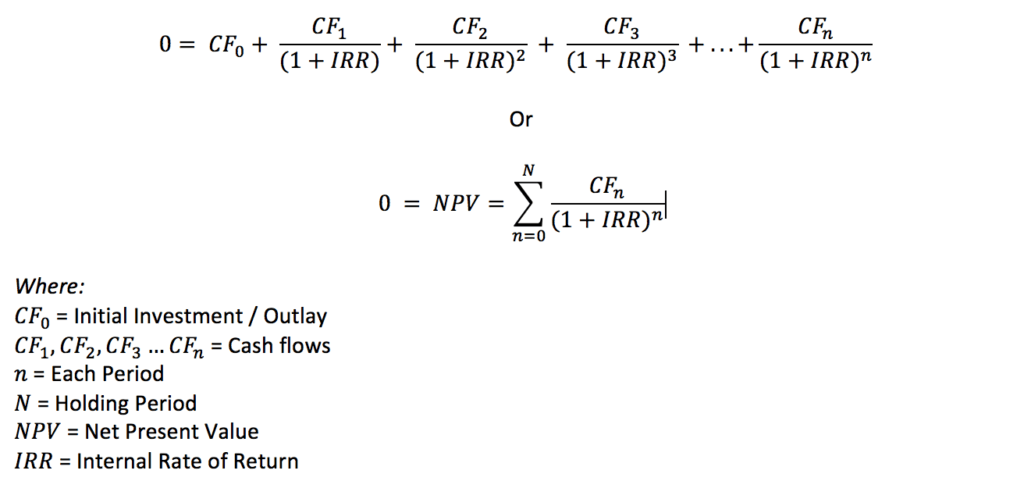
IRR= Li + [(Hi-Li) NPV at Li]/[NPV at Li-NPV at Hi]
where, Hi = Higher discount rate
Li = Lower discount rate
Decision criteria:
- For mutually exclusive project: IRR>Opportunity cost :- Project accepted.
- For non-mutually exclusive project : High IRR value :- Project accepted.
Merit
– It used to rank the project in descending order.
– It shows the maximum earning capacity of the project.
Limitation
– It cannot be used in mutually exclusive business.
– If DR exceed IRR than the NPV becomes –ve.