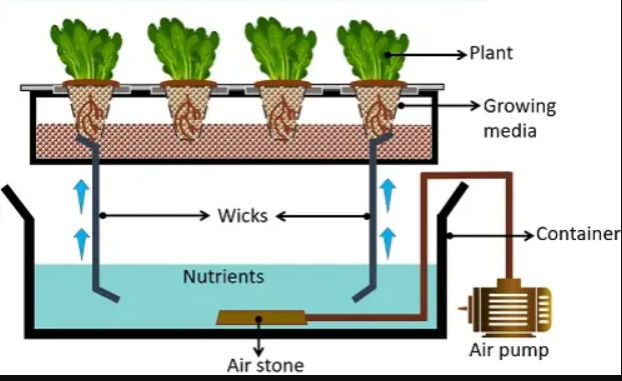
Wick system/ technique (Capillary movement)
- It is a very simple and low-maintenance type of hydroponic growing system.
- It uses a wick, typically made of cotton or absorbent material, to draw nutrient-rich water from a reservoir to the base of the plant.
- Plants are grown in a growing medium such as rock wool, clay pellets, or coco coir, and placed in containers or grow trays.
- The nutrient solution is stored in a reservoir below the container or tray, and the wick is placed in the bottom of the container or tray and extends into the reservoir.
- The wick absorbs the nutrient solution and transports it to the growing medium and roots of the plants.
Advantages of Wick System
- Low-cost and simple: Requires no electricity, pumps, or timers; easy for beginners.
- Passive system: Works on natural capillary action; no moving parts that can fail.
- Low maintenance: Minimal monitoring compared to active systems like NFT or Drip.
- Silent operation: No noise since there are no pumps or motors.
- Space-friendly: Suitable for small-scale indoor setups, classrooms, or hobby gardening.
- Good for small plants: Works well with herbs, leafy greens, and ornamentals.
Disadvantages of Wick System
- Limited nutrient supply: Wicking is slow and may not deliver enough water/nutrients for large or fast-growing plants.
- Not suitable for fruiting crops: Heavy feeders (tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers) can suffer nutrient deficiencies.
- Risk of salt buildup: Nutrients may accumulate in the growing medium over time.
- Overwatering/under watering issues: Poor wick material or medium can cause imbalance.
- Algae growth: Open containers can encourage algae on the surface of the medium.
- Less efficient: Compared to active hydroponic systems, plant growth is slower.