Autonomic nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system is part of peripheral nervous system which control involuntary activities of body.
- Regulated visceral organs
- Maintain homeostasis.
Types of autonomic nervous system and their arrangement
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Parasympathetic nervous system
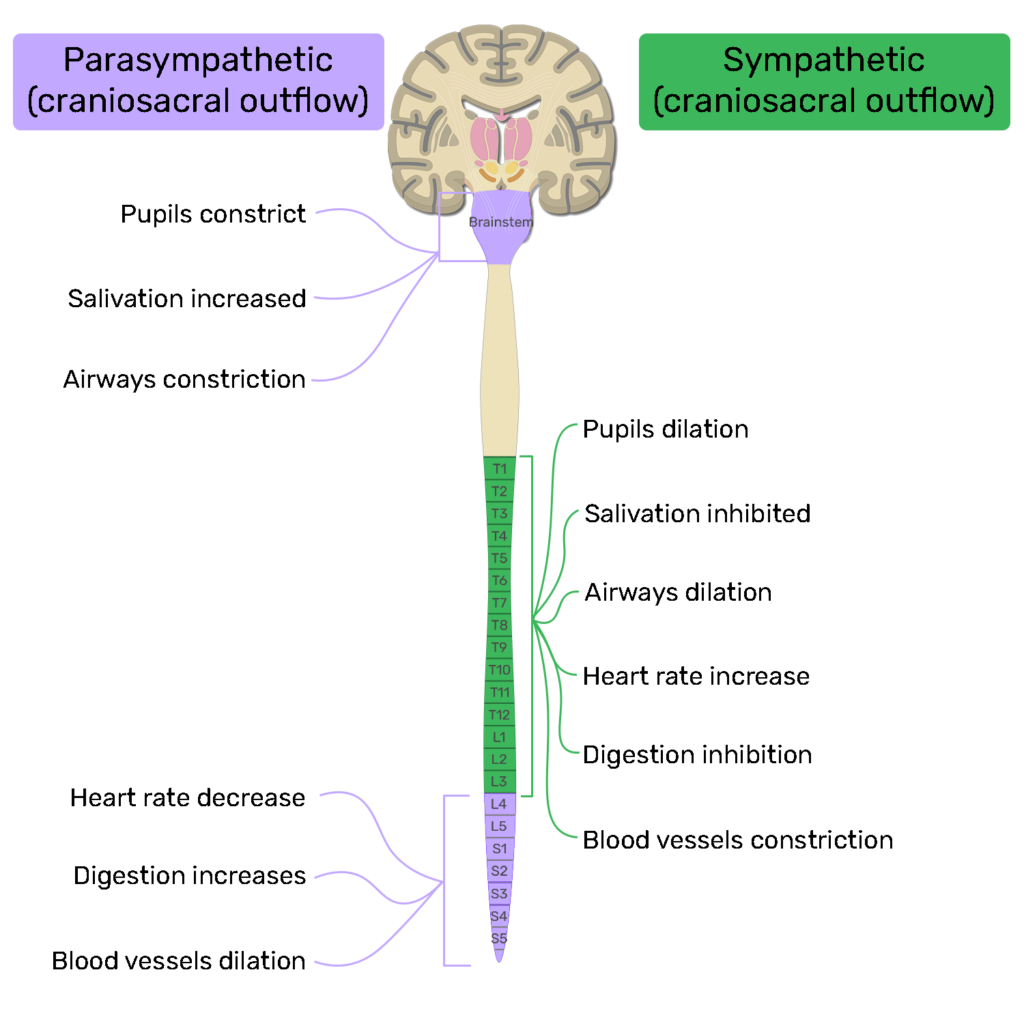
Sympathetic nervous system:
- It is formed of presympathetic /postsympathetic nerve fibre, collateral ganglia, and sympathetic cord.
- Smaller Presympathetic nerve fibre synapse with larger Post sympathetic nerve fibre.
- Collateral ganglia present near organ affected.
- Presympathetic nerve fibre release acetylcholine at synapses.
- This neurotransmitter is carried to postsynaptic neurons by receptors.
- Post synaptic neurons release non-adrenaline.
- Has excitatory effect (flight and fight response).
Parasympathetic nervous system
- It is formed of pre-ganglionic fibre, parasympathetic ganglia, and post ganglionic fibre
- Parasympathetic ganglia are present either near or inside organ affected.
- Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are larger than postparasympathetic neurons.
- Both ganglionic neurons are cholinergic in nature as they release acetylcholine at their nerve endings.
- Has inhibitory effects / (rest and digest response).