External ear
- Air filled cavity
- Formed of following parts
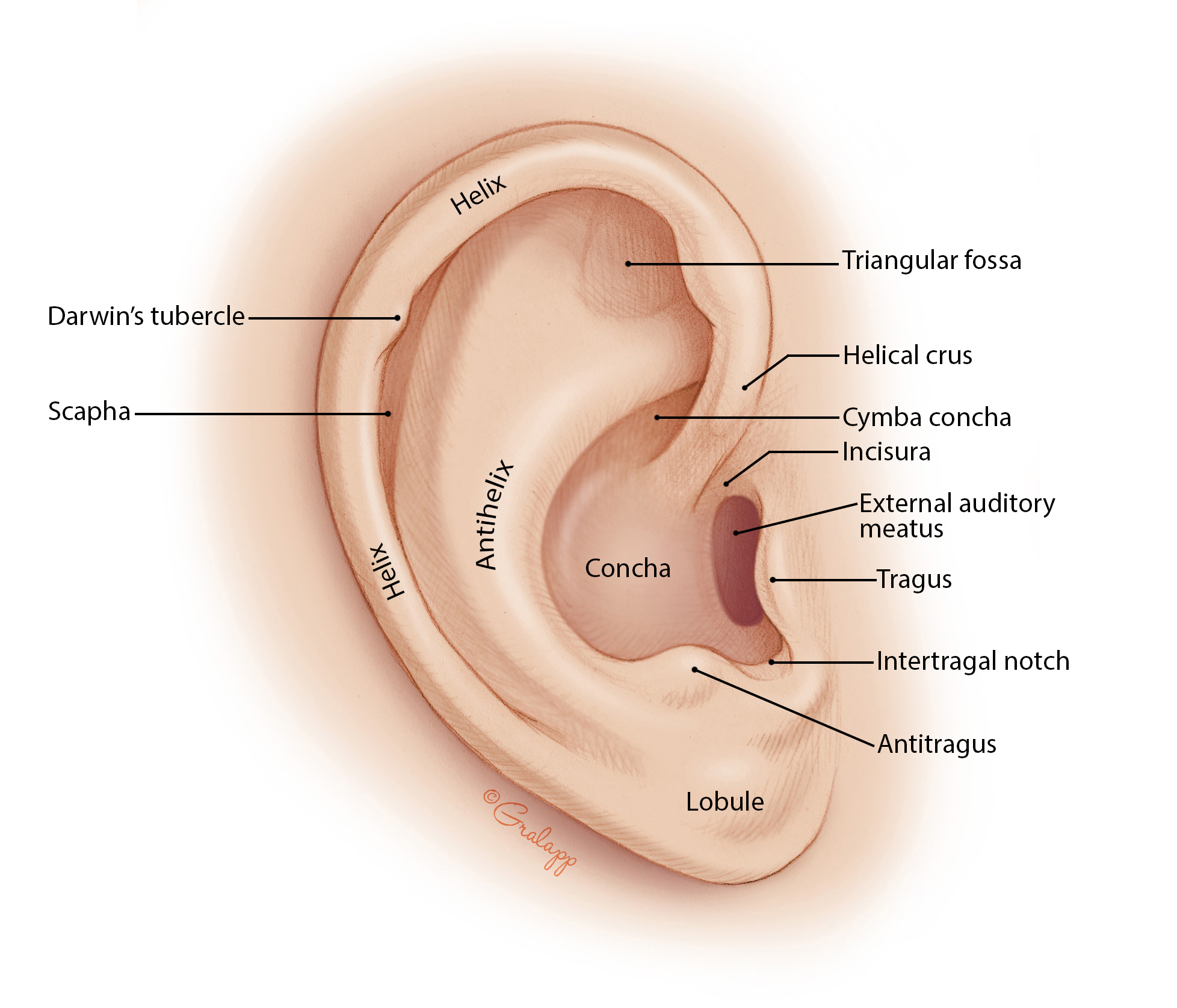
a. Pinna
- Roughly funnel shaped supported by cartilage
- Collect sound from different direction.
b. Auditory canal
- Long tubular and oblique canal.
- Concentrates sound to strike on ear drum
- Anterior 1/3rd supported by cartilage and posterior 2/3rd by bone.
c. Ear drum
- Separates external ear from middle ear.
- When sound strike on it, then it vibrate freely.
Middle ear
- Air filled cavity/tympanic cavity.
- Communicate with pharynx by Eustachian tube which maintains equilibrium.
- Tympanic cavity contains three bones articulating each other.
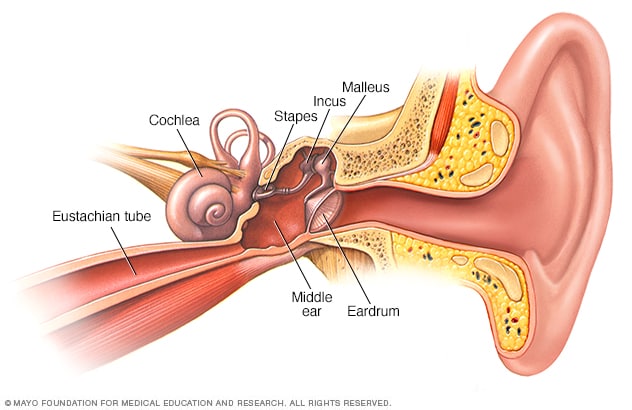
They are
a. Malleus
- Largest hammer shaped bone
- Connected with eardrum.
b. Incus
- Middle smaller bone, anvil shaped.
- Connected with malleus and incus
c. Stapes
- Smallest inner bone, stirrup shape
- Connected with oval window.
Internal ear
- Liquid filled cavity
- Formed of membranous labyrinth and bony labyrinth.
- Contains two parts:
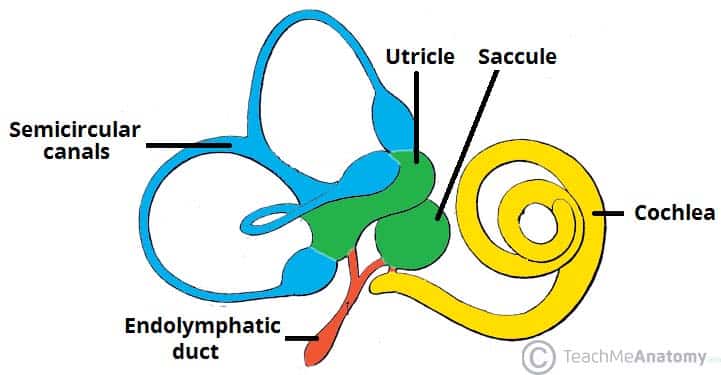
a. Vestibular parts
- Concerned with equilibrium filled with endolymph.
- Three semicircular canals converge.
- Works with visual system
b. Cochlear parts
- Concerned with hearing.
- Contains three canals
i. Vestibular canal
ii. Middle canal
iii. Tympanic canal
Middle canal contains organ of corti formed of numerous auditory phonoreceptors cells.