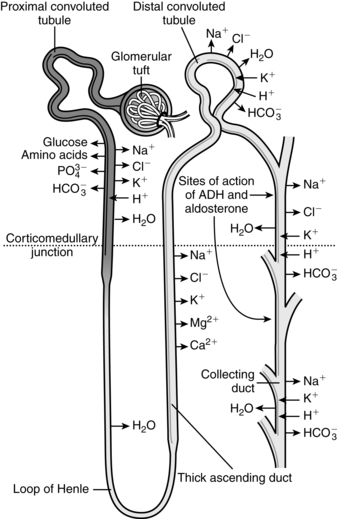
This is done by nephrons different parts like PCT, loop of henle, DCT and collecting tubule.
Sodium regulation
- When Na+ is high in blood, brain detected it and posterior pituitary gland inhibits the secretion of antidiuretic hormone
- Similarly, aldosterone secreted by adrenal cortex is decreased
- Decrease in ADH concentration means high urine production. High urine production suggests less reabsorption of sodium in blood. Thus high concentration of sodium ion is released through urine.
- Likewise, aldosterone is sodium saver. When it is inhibited, reabsorption of sodium is inhibited. Thus, more sodium along with water gets mixed with filtrate.
As a result, increase in urine production or decrease blood volume. In this way we get rid of sodium. If we have less Na+ concentration then process is reversed.
Potassium regulation:
- When K+ level is high in blood adrenal cortex stimulates aldosterone. This aldosterone helps to release potassium in urine.
- Similarly, drug diuretic furasamide in loop of henle change the permeability of cells i.e. inability to reabsorb sodium into blood. This is non potassium sparing.
Thus, potassium concentration increases in urine when K+ is high in blood.