Ability to smell is olfaction.
Olfaction processincludes different cells and their pathways:
- Olfactory tract
- Olfactory bulb
- Mitral cells
- Olfactory cells
- Glomerulus
- Sustentacular cells
- Bowmen’s capsule
- Olfactory cilia
- Olfactory cilia are sensory receptors that respond according to the chemical stimuli it received.
- Cilia reacts to stimuli and activate olfactory cells
- Bowmen’s gland produce mucous
- Now, axons of olfactory nerve pass towards olfactory bulb
Olfactory bulb lies over cribiform plate
- Secondary olfactory cells called mitral and tufted cells carry odorant and transmit it to olfactory tract.
- Olfactory tract transmit smell into three sites of brain
- Frontal cortex: conscious
- Hippocampus : odor memory
- Hypothalamus and amygdale: emotional and motivational
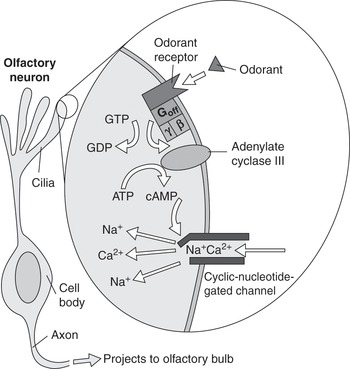
Excitation of olfactory cells
- Olfactory membrane when received odorant then it get diffuse to mucus
- This bind to receptor protein
- Receptor protein get bound with G-protein which activate adenylyl cyclase
- Here, ATP converts into AMP this opens sodium ions channel
- Now, action potential generate this excites olfactory nerve and it passes to CNS.