Synapse and transmission of nerve impulse, all or none character of nerve impulse, transmission of excitatory state from nerve to effectors tissue
Neurons
- Structural and functional unit of nervous system
- Neurons initiates and transmits nerve impulse to other cell
- Neurons are present in CNS, PNS and sensory organs
- Neurons consists of Dendrites, cell body, axon
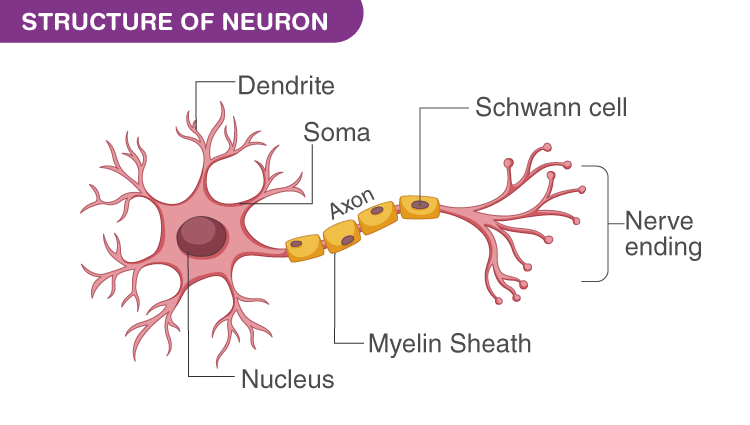
Primarily, contains dendrites, cell body and axon.
a. Dendrites
- Numerous, small, wide, fine branched like structure
- Carry impulse towards cell body
b. Cell body
- Core part of neuron
- Give rise to dendrites and axon
- Contain nucleus and other organelles
- Neurofibrils help to pass impulse to and from the cell body
c. Axon
- Single long processes
- Conduct impulse away from cell body
- Communicate with other neurons through synapse.
d. Terminal end
- Terminal part of axon which is neurosecretory in function.
#note
Myelinated nerve fibre:
- Axon surrounded by nerve fibre
- Sheath are interrupt at regular interval called node of ranvier
- Conduct nerve impulse at high speed
Non myelinated nerve fibre:
- Myelin sheath is absent
- Conduct nerve impulse at slower rate